* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRODUCT
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Music industry wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
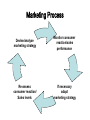
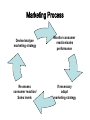
Letter of complaint → RB, p 77 Check out phrases on p 79 P 82, exercises 11 & 12 Exchange readers and compare TASK PRODUCTS AND BRANDS “BRAND” OR “PRODUCT”? • Anything capable of satisfying a need or a want. • A distinguishing symbol, mark, logo, name, word, sentence or a combination of these items that companies use to distinguish their product from others in the market. “U11: PRODUCTS AND BRANDS” (MK, p. 60) PARAGRAPH ONE: • HEADING? • DEFINITION of product? • EXAMPLES OF PRODUCTS? • PRODUCT LINE? • Other useful expressions? • EXPLAIN: Companies are... constantly reevaluating their product mix. • Why do companies’ product mixes regularly change? PARAGRAPH TWO • • • • HEADING? DEFINITION? OBJECTIVES OF BRANDING? HOW IS BRAND RECOGNITION ACHIEVED? • B2B? • B2C? • Other useful expressions? Do you recognize them? x 4 3 1 2 8 9 5 10 w z y 6 7 BEST GLOBAL BRANDS? Image? Feelings? Associations? • Which brands do you have an emotional attachment to because they represent your attitudes and feelings? PARAGRAPH THREE • HEADING? • CORPORATE BRAND NAME vs. INDIVIDUAL BRAND NAME – give examples • MULTI-BRAND STRATEGY – give examples – give reasons PARAGRAPH FOUR HEADING? BEST GLOBAL BRANDS WORTH OF A BRAND vs. COMPANY’S PHYSICAL ASSETS EXPLAIN: A company’s market value can be much greater than its book value. WHY? HW: Vocabulary p 61 Letter of apology • → RB, p 78 • p 82, exercises 13 & 14 HW: 1. Study RB pp 67 – 80 2. Do all tasks on pp 81-82 3. Revision: QUIZ (pp 83-85) 4. Write a letter of apology, RB p 78 Marketing, MK U 12, p 64 → MK p 64: Lead-in Selling vs. Marketing • Focus on: PRODUCT – selling – inward looking – out-dated – shorter – about profit now – introverted vs. CONSUMER ... ... ... ... … … Selling vs. Marketing • Focus on: PRODUCT – selling – inward looking – out-dated – shorter – about profit now – introverted vs. CONSUMER buying outward looking state-of-the-art longer time horizon about profit later extroverted The selling & marketing concepts • The “selling concept”: – You sell what you ________. • The “marketing concept”: – You make what ______________. • Marketers __________ needs, __________ and __________ new ones. • Examples of new “needs”: The selling & marketing concepts • The “selling concept”: – You sell what you make. • The “marketing concept”: – You make what will be bought. • Marketers satisfy needs, anticipate and create new ones. • Examples of new “needs”: – Walkman, video recorders, CD players, PCs, Internet, Google, mountain bikes, Facebook... Marketing Process Devise/analyse marketing strategy Monitor consumer reaction/sales performance Re-assess consumer reaction/ Sales levels If necessary adapt marketing strategy Marketing activities I • Identify/anticipate needs/wants of target consumers (market research): – internal research – secondary data – focus group interviews – quest. research – sales staff... • Analyze data II • Satisfy the needs better than the competition – strategic decisions about: – – – – product (design) pricing promotion distribution (placement) product (design, quality, features, style, brand name, size, packaging, services and guarantee) product (design, quality, features, style, brand name, size, packaging, services and guarantee) pricing (basic list price, discounts, length of the payment period, credit terms...) product (design, quality, features, style, brand name, size, packaging, services and guarantee) pricing (basic list price, discounts, length of the payment period, credit terms...) place (distribution channels, locations of points of sale, transport, inventory size...) Elements of the marketing programme (integration and the cost of it?) product (design, quality, features, style, brand name, size, packaging, services and guarantee) pricing (basic list price, discounts, length of the payment period, credit terms...) place (distribution channels, locations of points of sale, transport, inventory size...) promotion (advertising, publicity, sales promotion and personal selling) The Marketing Mix (The Four P’s) product (design, quality, features, style, brand name, size, packaging, services and guarantee) pricing (basic list price, discounts, length of the payment period, credit terms...) place (distribution channels, locations of points of sale, transport, inventory size...) promotion (advertising, publicity, sales promotion and personal selling) → MK, p 64, Vocabulary Reading: The product life cycle Marketing Process Devise/analyse marketing strategy Monitor consumer reaction/sales performance Re-assess consumer reaction/ Sales levels If necessary adapt marketing strategy Identifying market opportunities Market opportunities – profitable __________ of fillling unsatisfied ________ or creating _______ ones in areas in which the company is likely to be more successful than the _____________. Market opportunities are isolated by market segmentation. Market segmentation is a process of _________ a market into distinct _________ of buyers who have different __________ or buying _______. Identifying market opportunities Market opportunities – profitable possibilities of fillling unsatisfied needs or creating new ones in areas in which the company is likely to be more successful than the competition. Market opportunities are isolated by market segmentation. Market segmentation is a process of dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different requirements or buying habits. Target markets identified by market segmentation - BABY BOOMERS, X-GENERATION, Y-GENERATION, Z-GENERATION… - YUPPIES, GUPPIES, MILKIES, DUMPS, SWELLS, DINKS, SKIPPIES, BOBOS, FEMS, SINKIES, MINKIES, WOOPIES, KIPPERS… Market segmentation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. School Kids with Income and Purchasing Power Double Income No Kids Burnt-Out-But Opulent (people) Green Upward-mobile Professionals First-time Expectant Mothers Single Women Expect Lots in London Modest Introverted Luxury Keeper Young Upwardly-mobile Profesionals Downwardly-Mobile Professionals Single/Middle Income No Kids Well Off Older People Kids In Parents’ Pockets Eroding Retirement Savings REVIEW: What is ....? (Round 1) 1 A promise by a manufacturer or seller to repair or replace defective goods during a certain period of time 2 To introduce a new product onto the market 3 Attributes of a product: quality, price, reliability 4 A small specialized, but profitable market segment 5 The possibility of paying for a product over an extended period of time 6 The standard pattern of sales of a product over the period that it is marketed 7 The set of beliefs that the public at large holds of an organization 8 Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different requirements or buying habits What is ....? (Round 2) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Possibility of filling unsatisfied needs in sectors in which a company can profitably produce goods or services The extent to which an activity provides financial gain The sales of a company expressed as a percentage of total sales in a given market All the companies or individuals involved in moving a product from the producer to the consumer Wrappers and containers in which products are sold Consumers who buy various competing products rather than being loyal to a particula brand Collecting, analysing and reporting data relevant to a specific marketing situation (eg. a new product) An idea for a new product, which is tested with target consumers before the actual product is developed Identify the topic and match... • • • • • Internal Focus group Sales Printed sources of Questionnaire • • • • • secondary data research interviews research staff Sources of info in market research: • • • • • Internal research Focus group interviews Sales staff Printed sources of secondary data Questionnaire research Source of information involving... • contacting individuals by phone, mail or personally • business newspapers, magazines and trade journals, competitos’ annual reports, official government statistics... • invited members of the target market • data available in the company’s accounts and sales departments (record of sales, orders, inventory size) Source of information involving... • contacting individuals by phone, mail or personally – questionnaire research • business newspapers, magazines and trade journals, competitos’ annual reports, official government statistics... – printed sources of secondary data • invited members of the target market – focus group interviews • data available in the company’s accounts and sales departments (record of sales, orders, inventory size) – internal research UNJUMBLE AND ORDER: rearteil lersalhow mercosnu dropucer UNJUMBLE AND ORDER: retailer wholesaler consumer producer DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL Producer Wholesaler/distributor Retailer Consumer DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL Producer Wholesaler/distributor Online(Internet) Agent Retailer Own sales force Consumer → MK, p 66 or telephone or mail order sales











































![AnIntroductiontoMarketing[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008555155_1-1af3b70cfa03f8a4f7957dd38251412b-150x150.png)





