* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AnIntroductiontoMarketing[1]
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
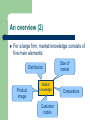
An Introduction to Marketing Module 4 A2 Business Studies According to Peter Drucker… “Marketing is not a function, it is the business seen from the customer’s pointer of view.” Objectives Definitions & Assumptions An overview of Marketing – – The need for marketing Market knowledge Where do you start? Segmentation Analysis Choosing your market strategy Integrated marketing Definitions & Assumptions Marketing is defined as: The process of learning about your customers & competitors, so that you can provide the right products at the right price in the in the right place, promoted in the right way to achieve your business objectives An overview (1) What does a business need to understand about its customers? – – – – Needs Wants Habits Attitudes In a small business, the owner may have direct contact with his or her customers, and fully understand the above A larger company may not have this closeness, and need to follow a different approach to marketing. An overview (2) For a large firm, market knowledge consists of five main elements: Distribution Product image Market knowledge Customer habits Size of market Competitors An overview (3) The size of the market: – Competitors – The value of purchases made by all the customers Market share, brand image, strengths & weaknesses Customer habits – – – Understanding the existing customers’ habits, likes, & dislikes. Their image of your product compared with rivals How loyal they are An overview (4) Product image – – Understanding the image and attitudes buyers of rival products have towards yours Why are they not buying your product? Distribution – Knowing the key distribution methods and outlets Where do you start? Facts and figures can be gained easily enough, however this an expensive and time consuming activity Gaining a genuine psychological understanding of the consumer is particularly difficult, requiring a much less black or white approach Segmentation Analysis A method of analysing the market place after having acquired a strong market knowledge. Involves identifying the key characteristics within the market Often reveals important sub-sectors in the market May highlight the different needs of consumers within a sub-group, which could then lead to a new product being identified. Segmentation Analysis (2) Demographically - according to the age structure of the population Geographically - by country or region or area Behaviouristically - according to the nature of the purchase, the use the product is put to, the loyalty to the brand and so on Benefit - according to the use and satisfaction gained by the consumer Socio-economically - according to social class and income levels Case Study: ICI Fertilisers How to decide what to do – Choosing your strategy… Important to have clear objectives The objectives must be optimistic, but realistically achievable – E.g. If the firm’s objective is to increase market growth from 15% to 25%, it is likely some serious investment in equipment and property is required. If the increase in demand never comes, the company’s security would be jeopardised. How to decide what to do – Choosing your strategy… After appropriate objectives are set, the organisation must identify the right strategy Often identify two or three alternative approaches, and then use market research to help make the choice Potential strategies… Marketing Objective Possible Marketing Strategies Increase the market share from 15% to 25% in 3 years Reposition To increase the proportion of sales coming from new products to 30% Increase Reduce Relaunch the proportion of over 60s among our market from 40% to 25% over the next 2 years Brand X into the mass market sector by cutting its price Launch new,upmarket high-price brands in each of next three years new product development budget by 50% and the market research budget by 30% the our product with livelier, younger packaging ad advertising Use direct mail to offer free samples to tose who have jut qualified to vote Keys to successful marketing Jump before you’re pushed – Exploit your assets – Successful marketing is about anticipating change not just reacting to it Asset-led marketing has the greatest level of long term success Keep aware of consumer psychology – Offering price cuts and discounts may be detrimental to the brand’s image Integrated marketing When a marketing decision is made, three questions must be asked: 1. Can we afford it? – 2. Can we produce it? – 3. Do the costs outweigh the benefits? Is the firm able to cope with an increase in demand? What knock-on effects may it have? – Could the brand/reputation suffer? An evaluation Marketing lies at the heart of every organisation, because firms have to be focussed on their customers if they want to succeed. Cynicism exists… – – Marketers essentially persuade people to buy things that they do not need This extends to companies such as Coca-Cola and Nestlé persuading people in developing countries to part with their small income on Western brands Conversely… – The range of goods in a supermarket is a tribute to successful marketing, it could be argued to have enriched people’s lives.