* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14 slides
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media and television wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Online advertising wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
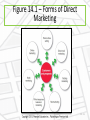
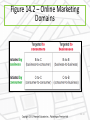
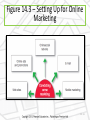
Direct and Online Marketing: Building Direct Customer Relationships Chapter 14 Rest Stop: Previewing the Concepts • Define direct marketing and discuss its • • benefits to customers and companies Identify and discuss the major forms of direct marketing Explain how companies have responded to the Internet and other powerful new technologies with online marketing strategies 14 - 2 Rest Stop: Previewing the Concepts • Discuss how companies go about conducting • online marketing to profitably deliver more value to customers Overview the public policy and ethical issues presented by direct marketing 14 - 3 First Stop: Facebook • Has tremendous impact and influence, not just as a sharing community but also as an Internet gateway • Has the potential to become one of the world’s most powerful and profitable online marketers • Entering the location based, deal-of-the-day online markets, and the banking business 14 - 4 Direct marketing • Connecting directly with carefully targeted segments or individual consumers, often on a one-to-one, interactive basis The New Direct-Marketing Model • For many companies today, direct marketing constitutes a complete model for doing business Companies such as GEICO have built their entire approach to the marketplace around direct marketing 14 - 6 Marketing at Work • Amazon is relentlessly customer-driven • Visitors receive a unique blend of benefits: huge selection, good value, and convenience Online pioneer Amazon.com does much more than just sell goods on the Web. It creates direct, personalized online customer experiences Direct Marketing Benefits to Buyers • • • • • Convenient Easy Private Immediate and interactive Access to a wealth of: • Products • Comparative information about companies, products, and competitors 14 - 8 Direct Marketing Benefits to Sellers • Building customer relationships • Offers sellers a low-cost, efficient, speedy alternative to reach markets • Online direct marketing results in lower costs, improved efficiencies, and speedier handling of channel and logistics functions 14 - 9 Direct Marketing Benefits to Sellers • Offers greater flexibility • Gives access to buyers that cannot be reached through other channels Southwest Airlines uses techie direct marketing tools—including a blog, DING! widget, and smartphone app—to inject itself directly into customers’ everyday lives—at their invitation Customer database • Organized collection of comprehensive data about individual customers or prospects, including geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data Customer Databases and Direct Marketing Best Buy mines its huge database to glean actionable insights on customer interests, lifestyles, passions, and likely next purchases. It uses this information to develop personalized, customer-triggered promotional messages and offers. Figure 14.1 – Forms of Direct Marketing 14 - 13 Direct Mail Marketing • Occurs by sending an offer, announcement, reminder, or other item directly to a person at a particular address • Well suited to direct, one-to-one communication • Permits high-target selectivity can be personalized, is flexible, and allows the easy measurement of results 14 - 14 Direct Mail Marketing • Traditional direct mail can be an effective component of a broader integrated marketing campaign Insurance companies like Farmers Insurance rely heavily on TV advertising to establish broad customer awareness. However, they also use lots of good old direct mail to communicate with consumers in a more direct and personalized way. Catalog Marketing • Marketing through print, video, or digital catalogs that are mailed to select customers, made available in stores, or presented online • Eliminate printing and mailing costs • Online catalogs offer • Unlimited amount of merchandise • Broader assortment of presentation formats • Real-time merchandising Catalog Marketing Digital catalogs: Days before the latest Lands’ End catalog arrives in the mail, customers can access it digitally at landsend. com , at Facebook, or via the Lands’ End mobile app 14 - 17 Telemarketing • Using the telephone to sell directly to customers • Marketers use: • Outbound telephone marketing to sell directly to consumers and businesses • Inbound toll-free numbers to receive orders from television and print ads, direct mail, or catalogs • Provides purchasing convenience and increased product and service information 14 - 18 Telemarketing Marketers use inbound toll-free 800 numbers to receive orders from television and print ads, direct mail, or catalogs. Here, the Carolina Cookie Company urges, “Don’t wait another day. Call now to place an order or request a catalog.” Direct-Response Television (DRTV) Marketing • Marketing via television, including direct-response television advertising (or infomercials) and interactive television (iTV) advertising Large, well-known companies—such as Kodak—are now using direct-response TV to get the message out directly to customers Kiosk Marketing • Product or service information and ordering machines are placed by companies in stores, airports, hotels, college campuses, and other locations Red box operates more than 27,000 DVD rental kiosks in supermarkets and fast-food outlets nationwide Online marketing • Efforts to market products and services and build customer relationships over the Internet Marketing and The Internet • Internet: Vast public web of computer networks that connects users of all types around the world to each other and an amazingly large information repository • Has given marketers a whole new way to create value for customers and build relationships with them 14 - 23 Marketing and The Internet • Click-only companies: Dot-coms, which operate online only and have no brick-andmortar market presence • Include e-tailers, search engines and portals, transaction sites, content sites, and online social networks • Click-and-mortar companies: Traditional brick-and-mortar companies that have added online marketing to their operations 14 - 24 Click-and-Mortar Marketing Staples backs its “that was easy” positioning by offering a full range of contact points and delivery modes 14 - 25 Online Marketing • Click-and-mortar business trends: • Almost all traditional companies have set up their own online sales and communication presence. • Many click-and-mortar firms are having more online success than their click-only competitors. 14 - 26 Figure 14.2 – Online Marketing Domains 14 - 27 Online Marketing Domains Business-to-Consumer (B-to-C) Marketing • Businesses selling goods and services online to final consumers Business-to-business (B-to-B) online marketing • Businesses using online marketing to reach new business customers, serve current customers more effectively, and obtain buying efficiencies and better prices Consumer-to-consumer (C-to-C) online marketing • Online exchanges of goods and information between final consumers Consumer-to-business (C-to-B) online marketing • Online exchanges in which consumers search out sellers, learn about their offers, initiate purchases, and sometimes even drive transaction terms Blogs • Online journals where people post their thoughts, usually on a narrowly defined topic Blogs • Offer fresh, original, personal, and cheap way to enter into consumer online conversations • Cluttered and difficult to control Purex used SocialSpark to help introduce its Purex Complete 3-in-1 Laundry Sheets via blogs such as Freaky Frugalite, Bargain Briana, 3 Kids and Us, and others that reach homemakers Figure 14.3 – Setting Up for Online Marketing 14 - 31 Corporate (or brand) Web Site • Designed to build customer goodwill, collect customer feedback, and supplement other sales channels rather than sell the company’s products directly You can’t buy anything at Nestlé’s colorful Wonka.com site, but you can learn about different Nestlé candy products or just hang around for a while and “feed your imagination.” Marketing Web site • Interacts with consumers to move them closer to a direct purchase or other marketing outcome Web Sites • Should be: • • • • • • • Easy to use Professional looking Physically attractive Useful Interactive Linked to other related sites Promotional Online advertising • Appears while consumers are browsing the Web Forms of Online Advertising Display ads • Appear anywhere on an Internet user’s screen and are often related to the information being viewed Search-related ads (or contextual advertising) • Text-based ads and links appear alongside search engine results on sites Content sponsorships • Companies gain name exposure on the Internet by sponsoring special content on various Web sites Viral marketing • Internet version of word-of-mouth marketing Online social networks • Online communities where people congregate, socialize, and exchange views and information Online Social Networks • Marketers can engage in these in two ways: • Participate in existing Web communities • Set up their own • Challenges of participating in existing Web communities: • Results are hard to measure • Such online networks are largely user controlled E-mail marketing • Sending highly targeted, tightly personalized, relationship-building marketing messages via e-mail Spam • Unsolicited, unwanted commercial e-mail messages E-mail can be an effective marketing tool. But there’s a dark side—spam, unwanted commercial e-mail that clogs up our inboxes and causes frustration. Mobile marketing • Marketing to on-the-go consumers through mobile phones, smartphones, tablets, and other mobile communication devices Marketing At Work • Marketers large and small are weaving mobile marketing into their direct marketing mixes Zipcar’s iPhone app lets members find and book a Zipcar, honk the horn (so they can find it in a crowd), and even lock and unlock the doors—all from their iPhone. 14 - 42 Public Policy and Ethical Issues in Direct Marketing • • • • Annoys customers Takes unfair advantage of impulsive buyers Internet fraud Phishing – Identity theft that uses deceptive e-mails and fraudulent Web sites to fool users into divulging their personal data • Online security • Access by vulnerable or unauthorized groups Public Policy and Ethical Issues in Direct Marketing Internet fraud has multiplied in recent years. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center provides consumers with a convenient way to alert authorities to suspected violations Public Policy and Ethical Issues in Direct Marketing – Consumer Privacy • Invades privacy • Ready availability of information leaves consumers open to abuse Public Policy and Ethical Issues in Direct Marketing – A Need for Action • Government agencies are investigating on: • • • • Do-not-call lists Do-not-mail lists Do-not-track lists Can Spam legislation • Congress is drafting legislation that would give consumers more control over how Web information is used Public Policy and Ethical Issues in Direct Marketing – A Need for Action • The FTC is taking a more active role in policing online privacy • In 2000, Congress passed the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), which requires Web site operators targeting children to post privacy policies on their sites • Many companies have responded to privacy and security issues with actions of their own Public Policy and Ethical Issues in Direct Marketing – A Need for Action By clicking on the little AdChoices advertising option icon in the upper right of this online ad, consumers can learn why they are seeing the ad and opt out if they wish Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concepts • Define direct marketing and discuss its • • benefits to customers and companies Identify and discuss the major forms of direct marketing Explain how companies have responded to the Internet and other powerful new technologies with online marketing strategies 14 - 49 Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concepts • Discuss how companies go about conducting • online marketing to profitably deliver more value to customers Overview the public policy and ethical issues presented by direct marketing 14 - 50 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 14 - 51