* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1_what is consumer behavior_fall09
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Professional practice of behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Home economics wikipedia , lookup
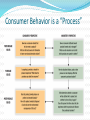
What is Consumer Behavior? Definition: the study of the processes involved when individuals or groups select, purchase, use, or dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy needs and desires. A PROCESS or Series of Steps: • Acquisition • Consumption • Disposing Consumer Behavior is a “Process” Areas of Consumer Behavior 1. Internal Factors = within the self Perception Learning Memory Personality Emotions Attitudes Motives 2a. Decision Making 2b. Situational factors Rational perspective Shortcuts Time constraints Retail environment Contexts 3. External Factors = outside the self Group influence Culture Subcultures Economic and Social Conditions Demographics Families and households Why is Theory Important in Understanding CB? A. Theory provides guidance 1. Overarching framework to explain behavior 2. Underlying principles explain observations 3. Hypotheses B. Theory allows us to make predictions about factual events based on our understanding of underlying principles. C. Pitfalls to avoid when studying CB 1. “Me” mentality 2. Single-minded explanation 3. Application only Applications of Consumer Behavior 1. Marketing Strategy competitive advantage reduce bad decisions Marketing Strategy Marketing strategies and tactics are based on explicit or implicit beliefs about consumer behavior. Decisions based on explicit assumptions and sound theory and research are more likely to be successful than are decisions based solely on implicit intuition. Knowledge of consumer behavior reduces the odds of bad decisions and market failures! Marketing Strategy and Consumer Behavior The Meaning of Consumption People often buy products not for what they do, but for what they mean Consumers can develop relationships with brands: Self-Attachment Concept Nostalgic Attachment Interdependence Emotional Bonds Applications of Consumer Behavior 1. Marketing Strategy 2. Public Policy protect consumers (e.g., FTC, FDA, SEC, EPA) consumer rights (safety, informed, redress, choice) Do Marketers Create Artificial Needs? Objective of marketing: create awareness that needs exist, not to create needs Need: a basic biological motive versus Want: one way that society has taught us that the need can be satisfied Are Advertising & Marketing Necessary? Does advertising foster materialism? Products are designed to meet existing needs; Advertising only helps to communicate their availability Advertisers are often blamed for promoting a materialistic society by making their products as desirable as possible. Do you agree with this? If yes, is materialism a bad thing? If no, what are your reasons? Applications of Consumer Behavior 1. Marketing Strategy 2. Public Policy 3. *****Social Marketing ***** drinking and smoking prevention literacy promotion charitable giving obesity prevent and/or exercise promotion environmental issues The Dark Side of CB Assume we are rational decision makers trying to maximize health and well-being of ourselves, families and society BUT Consumer terrorism Additive consumption Compulsive consumption Consumed consumers