* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patterns of Evolution
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
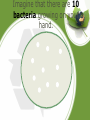
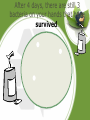
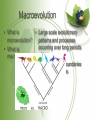
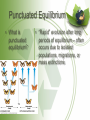
Patterns of Evolution Evolution Notes Part 3 • What is microevolution? – Evolution on a small scale within a single population • Natural selection is a mechanism for changes in populations that occurs when organisms with favorable variations survive, reproduce, and pass on traits to the next generation. • Artificial selection is the breeding of certain traits over others. Speciation • What causes • Reproductive isolation – when new species populations are prevented in to form? some way from reproducing with each other , their gene pools adapt and evolve separately, causing them to lose the ability to cross breed Reproductive Isolation • What causes • Geographic isolation – reproductive mountains, rivers, canyons isolation? • Temporal isolation – active or reproducing at different times of day or times of year • Behavioral isolation – differences in mating rituals that prevent reproduction between groups Anatomical • Some adaptations involve changes in the structure of body parts: mimicry and camouflage. – Mimicry enables an organism to copy the appearance of another species. MIMICRY Anatomical • Some adaptations involve changes in the structure of body parts: mimicry and camouflage. – Camouflage is a structural adaptation that enables an organism to blend in with its surroundings. CAMOUFLAGE Physiological Adaptations • Some adaptations are physiological or changes in an organisms metabolic processes. – Keep in mind that all things are made up of cells and the organelles are structurally and functionally similar in most organisms. Physiological Adaptations • Organisms are constantly changing to adapt to their environment. Take a look at organisms that have been exposed to antibiotic and pesticides. The organisms that survive have become selected because they are physiologically more resistant. Imagine that there are 10 bacteria growing on your hand. You use Germ-x to clean your hand everyday. After 4 days, there are still 3 bacteria on your hands that have survived. Is there anything special about these bacteria? Yes..they have something about their DNA that has made them different and strong enough to survive. So now what will happen? Those 3 that are “resistant” will undergo Mitosis. And after a week, your hands will be covered with tons of bacteria that are ALL resistant to Germ-X. Macroevolution • What is • Large scale evolutionary microevolution? patterns and processes occurring over long periods • What is of time macroevolution? • Transcends the boundaries of a single species Macroevolution • What are the 1. Extinction important topics 2. Adaptive radiation in 3. Convergent evolution macroevolution? 4. Coevolution 5. Punctuated equilibrium 6. Changes in developmental genes Extinction • Why is extinction important? • Several times in Earth’s history, mass extinctions wiped out ecosystems – During these events, many species became extinct – Other species took advantage of ecological opportunities as habitats opened up – This produced a burst of evolution Adaptive Radiation • What is adaptive radiation? • When a single species or group of species evolve through natural selection into diverse forms that live in different ways Adaptive Radiation • What are some • Darwin’s finches examples? • Wild mustard variations Convergent Evolution • What is convergent evolution? • Unrelated organisms in similar environments evolve to look remarkably similar to each other • What are some • Similarities between Australian marsupials and examples? placental mammals • Similarity in form between dolphins and sharks Coevolution • What is coevolution? • Two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time • What are some • Plants develop pollination methods that take advantage examples? of insect feeding adaptations, and vice versa Punctuated Equilibrium • What is punctuated equilibrium? • “Rapid” evolution after long periods of equilibrium – often occurs due to isolated populations, migrations, or mass extinctions Developmental Genes • What is meant by changes in developmental genes? • Homologous control genes serve similar functions in animals that have not shared a common ancestor in millions of years What should I believe? • Although evolution is widely accepted by scientists and had broad supporting evidence, it is still a theory • Remember, theories are well-supported testable explanations of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world • There are differences of opinion about interpretation and every person is entitled to his or her own opinion – the experts are not always objective • Our goal is to present the prevailing view and allow you to reach your own conclusions • Remember that everyone is entitled to their own opinion – yours is no more right nor wrong than anyone else’s