* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EVOLUTION!
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Spontaneous generation wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
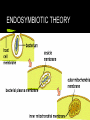
EVOLUTION! Many misconceptions All that it means= LIVING THINGS CHANGE OVER TIME TIME Origin of the universe- Big Bang?? Evidence? Yes- red shift, cosmic background noise Age of universe= 10-20 billion years Geologic time How old is Earth? Approximately 4.6 billion years old Many changes can occur Has Earth Changed? Yes Observe the continents- what do you notice? At one point all continents were together= PANGEA- http://geology.com/pangea.htm They began to split= Laurasia(north) and Gondwanaland (south) How did they move? Origin of Life? Spontaneous Generation Observation- meat left out to spoil, maggots develop Belief- maggots spontaneously arise Francesco Redi said ABSOLUTELY NOT! Redi’s Experiment- 1668 2 jars 1 with meat left open to air 1 with meat that is sealed Results? Maggots only in open jars Redi’s Exp. Step 2 People argued that air was necessary for spontaneous generation Redi seals jars with cloth to let air in but not flies Spallanzani’s Experiment-1775 People were still skeptical Boiled broth and placed in sealed flask No organisms develop- people still skeptical- no air in flask Louis Pasteur-1859 Uses swan neck flask Boils meat broth in flask and bends neck of flask into S shape Air can enter but airborne microorganisms cannot- they settled in the neck No microorganisms grew- FINALLY- no spontaneous generation- life comes from life BIOGENESIS How did life begin? 4.6 bya- earth was very different Atmosphere of methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, water vapor, but no free oxygen Intense solar radiation, lightning, volcanic activity First living organisms Possibly self replicating RNA molecules Eventually acquired a protective lipid coating Becomes something resembling today’s bacteria But how? Oparin’s Hypothesis Ancient earth’s conditions led to spontaneous formation of organic molecules (what are the main 4?) • These accumulated in oceans and combined into cells • http://vilenski.org/science/notebook/unit1 /historyoflife/oparin.html Miller-Urey Experiment Simulated conditions on ancient earth Successfully synthesized amino acids Confirms Oparin’s hypothesis Some holes in this idea Penn State Research- very new Organic compounds have been located in material in space (comets, meteorites, clouds of gas) Membrane forming molecules have been found in some meteorites Comets/meteorites bombard earth and give rise to life????? Problem? Oparin’s Idea Revisited- By PSU More evidence shows that first organisms were thermophilic (could thrive in earth’s early state) Life arises at bottom of ocean as thermophilic microorganisms So What happened next? Several Different Theories Endosymbiotic Theory Jean Baptiste De Lamarck- Acquired Traits Charles Darwin- Natural Selection Devries Gould ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY One Idea Organisms change over time by adapting Adaptations Structures/traits that are beneficial and serve a purpose to an organism or species Examples? Let’s go outside ACQUIRED TRAITS- Lamarck- Late 16th century Adaptations are acquired throughout and organisms life and passed on. Adaptations are results of organisms using or not using body parts. Acquired Traits INCORRECT! CHARLES DARWIN Takes a ride on the HMS Beagle. Stops @ Galapagos Islands- observes Finches http://worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys /samerica/galap.htm Comes up with theory of Natural Selection Darwin’s Ideas 2 Key Points Species of Organisms descended from common ancestors (adaptive radiation) “Descent with Modification” Natural Selection- best suited individuals survive and leave more offspring DARWIN-1859 THEORY OF NATURAL SELECTION established that change occurs in organisms without respect to need environment determines whether or not a variation improves the chance of survival change occurs gradually never said that man evolved from apes! infers that man and ape had a common ancestor THEORY OF NATURAL SELECTION Key Ideas OVERPRODUCTION plants and animals over produce limiting factors exist to balance populations and prevent extinction due to competition STRUGGLE FOR EXISTENCE competition exists for food and other resources food chains become established VARIATION individuals in a population vary- polygenic traits (humans, etc) they vary whether they need to or not some variations have an advantage in the environment SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST those with the variations best adapted to the environment will survive survivors reproduce and pass on traits to offspring ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCE ON EVOLUTION THE ENVIRONMENT DETERMINES IF A VARIATION WILL HAVE SURVIVAL VALUE THE ENVIRONMENT DETERMINES WHAT DIRECTION EVOLUTION WILL TAKE CHANGES IN ENVIRONMENT MIGRATION movement to a new environment- when 2 gene pools mix, new traits will emerge new mutations give offspring greater survival value WITHIN THE OLD ENVIRONMENT geologic impacts like volcanoes resistance to antibiotics, pesticides INDUSTRIAL MELANISM is a change in coloration caused by industrial pollution ISOLATION a split between interbreeding groups caused by geographic/physical barriers produces changes in behavior, color, which prevent them from breeding DEVRIES-1901 MUTATION THEORY OF EVOLUTION sudden changes in genes results in new types of plants and animals accounts for the variations suggested by Darwin mutations can be good, bad, or have no current value lethal genes which leaves organism with no chance of survival (almost always recessive) GOULD-1972? PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM agrees with Mutation Theory disputes Darwin’s gradualism-but not natural selection supports idea that evolution occurs in quick spurtsseen in fossil record all the time mutations accumulate over time and then a new species develops when there are too many differences between them there are no missing links SPECIATION SPECIES is a group of organisms that are similar in structure and can mate and produce fertile offspring--all have the same number of chromosomes CAUSES natural selection --mutations change in environment migration --isolation EVOLUTION OF A NEW SPECIES each generation inherits variations that are adaptive each generation forms new variations Gene Flow, Genetic Drift (chance) over a period of time, accumulations of variations will result in a new species if variations are unfavorable, the species will become extinct PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION ADAPTIVE RADIATION different species develop from a common ancestor CONVERGENT EVOLUTION organisms with different ancestors become more alike in shape, form, behavior... generally because they share the same environment EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION fossil record Homologous structures vestigial structures embryological evidence biochemistry Fossil Records fossils at various depths show different forms of life lineages of fossils of a particular group are found and quite complete Radiometric (radiation) dating of rock layers establishes a chemical connection between fossils Homologies similarities in structure and arrangement of parts indicates genetic relationships of common ancestor suggests environmental influences on adaptations selected Vestigial Structures structures of modern organisms with little to no function structures are often degenerate in appearance fossil evidence suggest structures once had a function Embryological Evidence similarities in development of the embryos of various organisms into differentiation of tissues currently, this view point is being scientifically challenged Biochemistry similarity of DNA in terms of identical genes similarity of hormones, digestive enzymes, ATP EXTINCTION OF THE DINOSAURS METEOR DISEASE CHANGE IN ENVIRONMENT NEW SPECIES ADDED COMPETITION RISE OF MAMMALS Mammals existed for 150 million years with dinos LOSS OF DINOSAURS OPEN NEW NICHES BETTER ADAPTATIONS CARE FOR YOUNG PLACENTA WARM BLOOD EVOLUTION OF MAN man is an animal man is subject to the rules of natural selection man changes over time A FINAL WORD most reasonable people (including the pope) understand that organisms evolve the argument is not over “IF” it occurs, but “HOW” it occurs belief that things change does not challenge religious belief