* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning Objectives and Outcomes
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
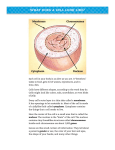
LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Learning Outcome 1= To annotate a cartoon to demonstrate the process of evolution Learning Outcome 2 = To annotate the spec handout with key terminology and definitions LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? You will need scrap paper and a pen / pencil LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Schools of thought Some psychologists like to stick to just one... LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? BIOLOGICAL HUMANISTIC BEHAVIOURIST COGNITIVE PSYCHODYNAMIC LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY BIOLOGICAL HUMANISTIC BEHAVIOURIST COGNITIVE PSYCHODYNAMIC LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Nucleus Chromosomes DNA Genes Charles Darwin Selective Breeding Evolution Natural Selection Sexual Selection Nature-Nurture KEY TERMS ARE A BIG PART OF PSYCHOLOGY, ENSURE YOU ALWAYS LEARN ANY KEY TERMS WE COVER IN CLASS LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Nucleus? Chromosomes? DNA? Genes? Charles Darwin? Selective Breeding? Evolution? Natural Selection? Sexual Selection? Nature-Nurture? LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Almost every cell in your body contains a nucleus (red blood cells are the only cells without a nucleus) LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Within each nucleus (apart from the sex cells) there are 46 of these structures, known as Chromosomes LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? The Chromosomes are made up of a chemical called DNA. The DNA carries units of information... LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? These units of information are called genes and these influence our bodily structure, function and BEHAVIOUR LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Nucleus Chromosomes DNA Genes Charles Darwin? Selective Breeding? Evolution? Natural Selection? Sexual Selection? Nature-Nurture? LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? In groups of 4 consider the stimuli around the room, some of you will be selected to explain your points to the rest of the class so be on your toes!! Mice and rats Bock and Goode (1996) Selective breeding LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Nucleus Chromosomes DNA Genes Charles Darwin? Selective Breeding Evolution? Natural Selection? Sexual Selection? Nature-Nurture? LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? In 1859 Charles Darwin published the Origin of the Species This states that all species of all living things have evolved over time from common ancestors through the process of natural selection LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? RANDOM physical and behavioural changes to a species either enable it to adapt to its environment and survive or they disadvantage it in some way and it dies out These ‘stronger genes’ which offer an advantage are passed onto the next generation and the ‘weaker genes’ die out This is just an example of natural selection specifically to do with attracting a mate E.g. A peacock has a very large cumbersome tail which has no purpose other than to attract a mate http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E1zmfTr2 d4c LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Complete your cartoon strip to show how the ‘rooting reflex’ behaviour in humans has evolved... Nucleus Chromosomes DNA Genes Charles Darwin Selective Breeding Evolution Natural Selection Sexual Selection Nature-Nurture? LO = What are the key features of the biological approach? Add the key words and definitions you have learnt today to your A3 specification sheet http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g3B8hS8 0k6A