* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multifactorial Traits - Study materials & Discussion
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Multiregional origin of modern humans wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Homo floresiensis wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Human mitochondrial genetics wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial Eve wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of human antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary origin of religions wikipedia , lookup
Homo erectus wikipedia , lookup
Craniometry wikipedia , lookup
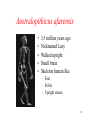
Anatomically modern human wikipedia , lookup
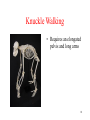
Homo heidelbergensis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Recent African origin of modern humans wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
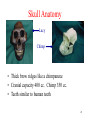
Human Evolution BIO 2343 Oklahoma City Community College Dennis Anderson Animal Connection • Humans share many traits with animals • We are most similar to apes – Same 206 bones – All but 3 of 650 muscles the same – DNA is 98% the same – Same blood types Albino Gorilla 2 Why are we so similar to apes? • Modern apes and modern man share a common ancestor who lived about 5 to 6 million years ago 3 Does the idea of human evolution from animals contradict a belief in God? • Many scientists of all religious faiths believe in both. • Some people feel evolution contradicts the literal interpretation of the Bible. 4 Earths Position in the Universe • 400 years ago the general public thought that the earth was the center of the universe – Sun revolves around the earth – The earth does not move 5 Galileo and Corpernicus • Demonstrated scientific evidence that the sun is at the center of our solar system and the earth moves around the sun 6 Galileo and the Church • Religious leaders felt the heliocentral theory (sun at the center) was a direct contradiction to the literal interpretation of the Bible • Galileo found guilty of heresy 7 Copernican System (Heliocentral Theory) • Did not destroy peoples belief in God • Public now accepts the overwhelming evidence for the heliocentral theory 8 Theory of Evolution • Science has overwhelming evidence that all life is constantly evolving 9 Natural Selection • One mechanism of evolution • Main concepts of natural selection – – – – Overproduction of offspring Inherited variation in offspring Competition Best adapted in a given environment survive and reproduce to increase their kind • They are naturally selected 10 Overproduction of Offspring • Elephants (very slow reproductive rate) – If all the offspring of one elephant pair survive and all their offspring survive then: • 750 years = 19,000,000 elephants • 1200 years = Enough elephants to cover the earth! • Beetles – A handful that weighs 10 mg each – 82 weeks • 61,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 ton – The weight of the earth! 11 Variation of Offspring • Offspring of the same parents are different from each other 12 Competition • Since more individuals are born than can survive for an extended period of time, they compete for resources – Food – Living space – Mates 13 Best adapted to a given environment are selected to survive • Brown bears – Adapted to survive in Oklahoma • Polar bears – Adapted to survive in Alaska 14 Sequence of Human Evolution • Hundreds of fossils have been found • Some of the major fossils will be discussed in this presentation 15 Australopithicus afarensis • • • • • 3.5 million years ago Nicknamed Lucy Walked upright Small brain Skeleton human like – Feet – Pelvis – Upright stance 16 Comparative Anatomy Lucy Gorilla Human • Gorilla pelvis adapted for knuckle walking • Human pelvis adapted for upright walking • Lucy’s pelvis very similar to human pelvis 17 Knuckle Walking • Requires an elongated pelvis and long arms 18 Lucy’s pelvis allowed her to walk like a human instead of an ape. 19 Fossilized Footprints • Footprints left when a a pair of Australopithecines walked in the ash of a recently erupted volcano 20 Skull Anatomy Lucy Chimp • Thick brow ridges like a chimpanzee • Cranial capacity 400 cc. Chimp 350 cc. • Teeth similar to human teeth 21 Lucy: A Transitional Fossil • Transitional fossil shows characteristics of two kinds of animals – Represent the transition from one organism to another • Ape characteristics – Skull – Cranial capacity • Human characteristics – Walked upright – Feet – Pelvis 22 Australophithicus africanus • 2.8 million years ago • Cranial capacity 460 cc 23 Homo habilis • Cranial capacity 630 cc • Flatter face than Australopithecines • Used tools – Nicknamed handy man 24 Homo erectus • 1.8 million to 35,000 years ago • 1,000 cc cranial capacity • Large brow ridges • Sloping forehead • More advanced tools than H. habilis 25 Homo erectus • Skeleton very similar to modern man • Used fire • Traveled – Fossils found in Africa, Europe, China, Indonesia 26 Homo neanderthalensis • 135,000 to 25,000 years ago • Cranial capacity up to 1750 cc – Larger than modern man • No chin • Sloping forehead • Buried dead with tools and flowers 27 Homo sapiens • 200,000 years ago to present – Photo is a skull 100,000 years old • 1400 cc cranial capacity • Vertical forehead • Pronounced chin 28 Modern Homo sapiens • Small front teeth • Small brow ridges • Rounded cranium 29 Sequence of Human Evolution One of several possibilities Homo neanderthalensis Australopithicus afarensis Australopithicus africanus Common ancestor Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo sapiens Modern apes 30 Evolution of Skull • • • • • Cranial capacity increases for a larger brain Face become flatter Brow ridges become smaller Forehead becomes higher Chin develops 31 Tools used to learn about our evolutionary past • • • • Study of fossils Comparing DNA Comparing chromosomes Comparing protein sequences 32 Paleontology • Study of fossils – Allows us to see anatomical similarities between us and organisms that lived in the past – Allows us to see how our ancestors have changed over time 33 Comparing DNA • Human DNA compared to: – – – – Chimpanzee 99% same Gorilla 97.7% same Orangutan 96.3% same Another human 99.9% same 34 Comparing Chromosomes • All apes have 48 chromosomes • Chromosome bands between human (H) and chimpanzee (C) 99% the same • Translocation of two ape chromosomes formed human chromosome 2 35 Inversions • Human and chimp chromosomes • Inversion between p14.1 and q14.1 • 9 total inversions in human vs. chimp 36 Comparing Protein Sequences • Many proteins in all of man are identical • Organ transplants require similar proteins in the donor and the recipient – A sibling or parent is often the best source for an organ transplant 37 Which would be the closest protein match for an organ transplant? Assuming all are alive and healthy. • A persons father • A persons great grandfather • A persons 10th great grandfather 38 Molecular Clock • The further you go back in time, the more proteins (and DNA) are different. • Differences in protein sequences and DNA can be used to estimate time when two species shared a common ancestor 39 Related Organisms • Close similarity of protein sequences indicates close relationship 40 Cytochrome C • Protein used to release energy from food • 104 amino acids • 20 of the amino acids occupy the same position in all eukaryotes 41 Comparison of Human Cytochrome C • 100 amino acids different in tuna fish • 12 amino acids different in a horse • 8 amino acids different in a kangaroo • 1 amino acid different in a monkey • Identical to chimpanzee 42 Mitochondrial DNA • Only inherited from mother • Mutates faster than nuclear DNA – Lacks repair enzymes 43 Mitochondrial DNA • Studied in several different human populations • Greatest diversity found in African population – Therefore the oldest population • Molecular clock 44 Mitochondrial Eve • Mother of all humans • She may have lived about 200,000 years ago in Africa 45 Native American Origin • Four Rare mtDNA haplotypes are found in Native Americans • The same haplotypes are found in Mongolia and China 46 Mitochondrial DNA • Four Rare mtDNA haplotypes are found in Native Americans • The same haplotypes are found in Mongolia and China 47 Neanderthal Man • Mitochondrial DNA studies indicate he was not a direct human ancestor • Contemporary species with early Homo sapiens • H. sapiens out competed H. neaderthalensis 48 Eugenics • “Improvement” of the human race • Attempt to direct human evolution – Not allow unfit to reproduce – By 1956 58,000 people in USA sterilized for being feeblemindedness, criminality and insanity 49 American Eugenics Society • Founded in 1923 • Lobbied for IQ tests of immigrants • Lobbied to not allow immigrants from countries not from northern Europe 50 Fitter Families Exhibit • State fairs across the nation • Promoted eugenics 51 Eugenics Champion • Hitler wanted to improve the human race • killed millions of people in the name eugenics 52 The End 53