* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Study Guide Answers
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
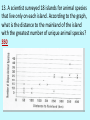
Evolution Study Guide Answers 1. EVOLUTION refers to the phenomenon where changes are noticed in a species over time. 2. CHARLES DARWIN developed the theory of natural selection based on his observations of plants and animals on the Galapagos islands. This theory supported the ideas of evolution. 3. NATURAL SELECTION is a theory that explains evolution. It relates to the phrase “survival of the fittest” because it shows that individuals with characteristics suited to an environment will survive and have a better chance of reproducing. Organisms without these characteristics will not be able to reproduce and therefore will die. (Example: giraffe neck length and pepper moths of Manchester) 4. TRUE or False. The changes that occur during natural selection are due to genetics. 5. A THEORY is a well tested concept that explains a wide range of observations. 6. Circle the options that provide evidence for evolution. similarities in DNA sequences, similarities in embryos, fossils , similarities in body structure 7. True or False. A change in a single organism over time is an example of evolution. 8. Fossil are the preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. 9. According to the diagram below, which layer of soil would contain the youngest fossils? Layer A 10. A characteristic that enables an organism to live more successfully in its environment is a(n) Adaptation. 11. A group of similar organisms that can mate with one another and produce fertile offspring is a Species. 12. The body color of a moth can vary just as height among humans can vary. These differences between members of the same species are known as Variation. 13. A scientist surveyed 18 islands for animal species that live only on each island. According to the graph, what is the distance to the mainland of the island with the greatest number of unique animal species? 350 14. Due to a drought in the giraffe’s habitat, only the giraffes with the longer necks were able to get the food they needed. This meant that giraffes with shorter necks were at a disadvantage. In order for the giraffe species to beat extinction, should the females choose mates with longer necks or mates with shorter necks? Explain your answer based on what you learned about evolution. They should choose mates with longer necks, their babies will have a higher chance of having long necks, being able to eat from the trees, they have a better chance to survive and reproduce 15. Which animals are more closely related: raccoons and lesser pandas or lesser pandas and giant pandas? 16. When did giant pandas and bears evolve from their common ancestor? 10 M.Y.A 17. Which animal would have DNA that is most similar to lesser pandas? Raccoons 18. When a species produces more offspring than it has resources, this is known as Overproduction 19. If there are more organisms than resources, Competition will occur between members of the same species. This does not mean animals of the same species will fight one another but simply that some will find enough to eat while others will not. 20. What are the four parts of natural selection? Overproduction, competition, variations, selection 21. Explain the term homologous structures. If two organism have homologous structures they have common Ancestor 22. In modern times, where does MOST evidence for evolution come from? DNA 23.What is the difference between camouflage and mimicry? Camouflage-blends in with environment; mimicry- copying another organism’s look 24. What is the difference between gradualism and punctuated equilibrium? Gradualism- theory that states evolution happens slowly over time. Punctuated equilibrium-theory that states organisms evolve in short periods of rapid change 25. Where are the oldest fossils found? A. In the bottom layers of rocks. B. In the top layers of rocks. C. In the middle layers of rocks. D. In museums 26. Why did the peppered moths evolve? The industrial revolution caused the trees to change colors (darker) and those moths that were darker, survived and passed on their traits. 27. Why did the Galapagos finches evolve? The finches were separated on the different islands and had different types of food to eat. The finches with beaks that could easily eat the available food survived and passed their traits. 28. If a population cannot adapt to their changing environment, what will eventually happen to them? They will go extinct. 29. Evolution is the change of a species over time. Natural Selection is those who are best suited to the environment survive pass on their traits. 30. The mammoth