* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
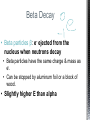
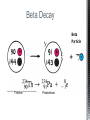
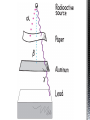
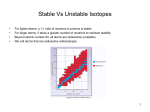
http://memekid.com/funny-pictures-about-going-back-to-school.htm Mass Energy Atomic Number Atomic Mass Atomic Charges Radioactivity Radioactive decay Half-life Ionizing-Radiation Alpha Decay Gamma Decay Beta Decay Excited State Ground State Isotope Fusion Fission Transmutation Nuclide Law of Conservation of Mass Law of Conservation of Energy Einstein’s E=MC2 How does a nuclear reactor work? At nuclear power plants, the heat to make the steam is created when uranium atoms split – called fission. There is no combustion in a nuclear reactor. Here's how the process works. Pressurized Water Reactors (also known as PWRs) keep water under pressure so that it heats, but does not boil. http://www.lanl.gov/science/1663/images/reactor.jpg How does a small mass contained in this bomb cause…… • Nuclear Bomb of 1945 known as “fat man” http://www.travisairmuseum.org/assets/images/fatman.jpg …this huge nuclear explosion? http://library.thinkquest.org/06aug/01200/Graphics/705px-Nuclear_fireball.jpg Like this • Starting nuclear chain reactions = releases a huge amount of energy (E) • Per unit volume, an atom bomb may be millions or billions of times more powerful than TNT. • Nuclear reactions (rxn) occur: neutrons r fired @ closely packed atoms w/ heavy nuclei (uranium or plutonium isotopes). • The heavy nuclei break apart into lighter nuclei (fission) when hit by a neutron, then it generates more neutrons which bombard other nuclei, creating a chain reaction. • Breaking the nuclei rather than releasing E thru a regular chem rxn, atom bombs can release more than 80 terajoules of E per kilogram (TJ/kg). • Fusion releases E by fusing together nuclei rather than breaking them apart. Notation Isotopes • Atoms of a given element with: same #protons but different # neutrons H H H http://education.jlab.org/glossary/isotope.html Isotopes of Carbon Radioactive Isotopes • Isotopes of certain unstable elements that spontaneously release (emit) particles and E from the nucleus. 3 Main Types of Radioactive Decay • Alpha α • Beta β • Gamma γ Energy Alpha Decay Emission of alpha particles α : • helium nuclei • two protons and two neutrons • can travel a few inches through air • can be stopped by a sheet of paper, clothing. • Low E Alpha Decay Alpha Particle Uranium Thorium Beta Decay • Beta particles β: e- ejected from the nucleus when neutrons decay • Beta particles have the same charge & mass as e-. • Can be stopped by aluminum foil or a block of wood. • Slightly higher E than alpha Beta Decay Beta Particle Thorium Protactinium Gamma Decay • Gamma radiation γ : electromagnetic (EM) E that is released. • Gamma rays r (EM) waves. • no mass/charge. – Most Penetrating, can be stopped by 1m thick concrete or a several cm thick sheet of lead. • Ultra High E