* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Evolution Chapter 10 Honors
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
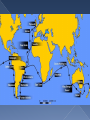
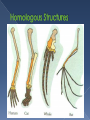
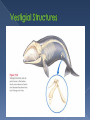
1785- James Hutton 1798-Thomas Malthus 1809- Jean Baptiste Lamarck 1831 to 1835- Voyage of the H.M.S. Beagle 1833- Charles Lyell 1858- Alfred Wallace 1859- Charles Darwin Geologist Proposed that the Earth was millions (not thousands) of years old Based on the processes of rock upheaval (uplift) and weathering Economist Proposed that humans would run out of resources like food and space if the human population numbers continue to grow If food and space are scarce, there will be competition for them French naturalist Proposed one of the first theories about how species change over a period of time (evolution) In Lamarck’s theory, individuals evolved Three Principles › Tendency Towards Perfection Innate tendency towards complexity and perfection › Use and Disuse Organism develops new adaptation by using the structure more Organism loses an adaption by not using the structure › Inheritance of Acquired Traits Traits acquired by an organism can be passed on to the next generation Geologist Published “Principles of Geology” Also proposed that the Earth is very old Proposed the forces at work in geology today are the same forces that have shaped the structures throughout time on Earth This had to take a long time Naturalist Independently proposes theory of evolution Writes Darwin about theory prompting him to publish his theory formed many years before Born the same day as Abraham Lincoln Studied theology in college Became the naturalist aboard the H.M.S. Beagle Proposed theory of evolution based off of observation from that trip Published theory in On the Origin of Species in 1859 Sailed from England Traveled to › South America › Africa › Australia › New Zealand › Galapagos Darwin studied › Difference within and between species › Living specimens › Fossils › Geology Group of islands off the coast of South America Each island has a unique climate Darwin observed › Marine iguanas › Tortoises › Finches Variation › Individuals naturally vary from each other › Variations that are genetically based can be passed on from one generation to the next (although Darwin did not know how) Struggle for Existence › Most populations grow past their resources › Organisms within a population must compete for their share Food Space Mates Other necessities Survival of the Fittest (Natural Selection) › Organisms have adaptations (inherited variations) that make them a good match to their environment (fitness) › Individuals with better fitness survive longer and reproduce more therefore passing on their genes › Future generation have more individuals with the well-fitted adaptation › It is about reproduction not survival!!! Survival › › › › › Camouflage Bright coloration Big Size Heightened senses Behavior Reproduction › Big size › Costly structures › Behavior Artificial Selection › Most fit adaptations are based on human choices › Individuals are bred to pass on desired traits Descent with Modification › Individuals have common descent › Evolution over a long period of time diversifies species › All species descend from common ancestor › Cladograms- diagram showing evolutionary relationships Fossil Record › Darwin knew fossils represented dead organisms › Also knew that newer organisms were closer to the top › Record showed evidence of change over time Geographical Distribution of Living Species › Beaks of Galapagos Finches › Neck Length and Shell Shape for Tortoises › Various Variations for Marine Iguanas › Pattern of Organisms in Similar Environment Homologous and Vestigial Body Structures › Homologous Structures that develop from the same embryonic tissues Mature forms often have similarities but may look different and have different functions › Vestigial Structures that no longer have a function for an organism but are still present Embryology › Many embryos look similar to each other during development and develop in similar ways Study of Evolution at the DNA or protein levels Problem - related species have similar DNA sequences Related species share a common ancestral DNA. The closer the relationship, the more similar the DNA sequences should be.