* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download San Francisco Bay: Interfacing ocean and rivers through
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Sea level rise wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
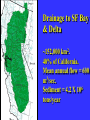
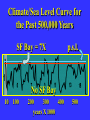
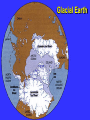
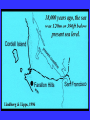
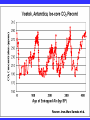
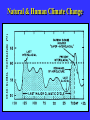
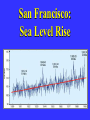
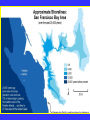
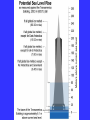
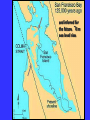
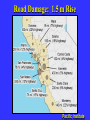
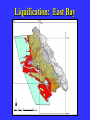
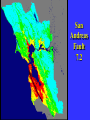
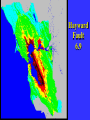
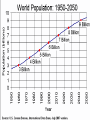
“Civilization exists by geological consent . . . subject to change without notice!” Will Durant, 1926 San Francisco Bay Through Time Jere H. Lipps, UCMP Berkeley San Francisco Bay Largest estuary west Americas. 300+ sq mi Ave. depth=18 ft Drains much of California. 7 million people live in area. Large industrial base. San Francisco Bay & Delta A very shallow, ephemeral estuary Drainage to SF Bay & Delta ~152,000 km2. 40% of California. Mean annual flow = 600 m3/sec. Sediment = 4.2 X 106 tons/year Human Impacts (years ago) • • • • 13,000: Arrival by sea and/or land 8,000: Began harvesting the new bay 2-3000: Built shell mounds 250: Europeans arrived; Native Americans declined • 160: California won from Mexico, Gold Rush • 135: Bay filling began • 100: Industrialization and development began in earnest > 100: Industrial global warming Subject to: Sea level changes. Earthquakes. Devastating fires. Population increase. Pollution. Invasions. History Matters! Conservation, Ecology and Evolutionary Biology as Historical Sciences What We Can Control • • • • • Radioactivity Destruction of Habitats Chemical Pollution Genetic Depletion Climate Change What We Cannot Control • • • • • • Plate Tectonics Sedimentation* Global Climate Change* Glacial Melting Sea Level Changes Natural Changes in Geology & Biology* What’s the Problem? Nature Us California: Always Changing From Hall 2005 Climate: Always Changing High Latitude Temperature Changes Inferred from Deep Sea Isotopic Records Zachos et al. 2001 Temp C: 0 4 8 12 How Do We Know? Oxygen isotopes of ice or microfossils • • • • • • • 16O, 17O and 18O 8 protons 8, 9 and 10 neutrons = different masses Each behaves differently Warmer water = more 18O More ice = more 18O d18O Earth to Sun Relationship: Orbit, Tilt, Equinoxes Interglacials Glacials Climate/Sea Level Curve for the Past 500,000 Years SF Bay = 7X p.s.l. No SF Bay 10 100 200 300 400 years X 1000 500 Mostly, SF Bay was a river valley Glacial Earth What is Global Warming? • Certain gases in atmosphere trap heat, like in a Greenhouse. • CO2, CO, CH4, NO, & others. • Contributed by volcanoes, some other sources, and now human activities. • Nature can’t remove it fast enough. • Atmosphere & ocean linked. Both warm, not necessarily smoothly. • Venus & Mars are Greenhouse planets. Greenhouse Gases • • • • • • Water Vapor Carbon dioxide Methane Chloroflourocarbons Ozone Nitrous oxide H2O CO2 CH4 (CFCs) O3 NO The Carbon Cycle • An atmosphere - terrestrial biosphere loop. • A terrestrial biosphere- geospherehydrosphere loop. • An atmosphere-geospherehydrosphere loop. Temperature & CO2 Variations Last 420,000 years Temperature & CO2 Variations Last 18,000 years Temperature & CO2 Variations Last 50 years Greenhouse Changes Natural & Human Climate Change Courtesy of Ken Towe Greenhouse Effects 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Increasing CO2 Increasing H2O: Flooding Increasing El Nino events Increasing temperature: 8-12OC Sea level rising: Up to 8+ m Increased hurricane & tornado occurrence/intensity 7) Redistribution of crops & species 8) Increasing diseases 9) Major changes in oceans & biotas Patagonia: Always Changing Glacial Retreat 80 m since 2000; more to come in next 30 years San Francisco: Sea Level Rise Potential Sea Level Rise East Antarctica 26,039,200km3 West Antarctica 3,262,000km3 Antarctic Peninsula 227,100km3 Greenland 2,620,000km3 All other ice 180,000km3 TOTALS: 64.80m 8.06m .46m 6.55m .45m 32,328,000km3 80.32m When? 1000’s of years: Natural variations. 100’s of years: Human effects. 10’s of years: Sudden release of CH4 clathrates, Catastrophic collapse of ice sheets. and inferred for the future. ~8 m sea level rise. Road Damage: 1.5 m Rise Pacific Institute Fire Hazard Will Increase East Bay Fires History • Fire is a natural part of the East Bay environment • Major fires have occurred every 10 to 15 years in the East Bay hills • • • • • • • • • • 1923: 130 acres , 584 homes 1931: 1,800 acres, 5 homes 1933: 1,000 acres, 5 homes 1937: 700 acres 1946: 1,000 acres 1960: 1,200 acres, 2 homes 1970: 204 acres , 37 homes 1980: 2 acres, 5 homes 1990: 200 acres 1991: 1,700 acres, 3,400 homes, 25 died • 1995: 3 homes • 2002: 5 acres The 1923 Berkeley Fire Destroyed 584 Homes in 2 HOURS Oakland Hills Fire from space NASA Losses 1991 Oakland Hills Fire • • • • • 25 Dead 150 Injured 3,471 Homes Lost 1,520 Acres Burned Largest Fire Loss in the history of the nation up to that time - $2.2 billion • Economic Loss: 15-20% business failure in nearby retail, citywide unknown 1910 2003 Tilden Park Source: Jean Quan Living in the Hills Each arrow = house Source: Jean Quan San Andreas Fault System >60% chance of a 6.7 quake in next 30 years in Bay Area Ten Greatest Quakes A Few California Quakes • • • • • • • • • San Francisco Calaveras fault Imperial Valley Kern County San Fernando Coalinga Loma Prieta Northridge Parkfield 1906 1911 1940 1952 1971 1983 1989 1994 2004 8.25 6.5 7.1 7.7 6.5 6.5 7.1 6.7 7.0 Oak Knoll Hospital 1971 Bay Area Faults Probability of Earthquakes > 6.7 2003-2032 = 62% USGS http://quake.usgs.gov/ Rock Type Makes a Difference Liquification: East Bay San Andra San Andreas Fault 7.2 Hayward Fault 6.9 University of California, Berkeley UCB Memorial Stadium You Need an Earthquake Bucket!! The Real Problem A World Full of Humans 1960 = 3,000,000,000 2007 = 6,650,189,946 2040 = 8,900,000,000 This in your lifetime! In Your Kids’ Lifetime • • • • • • • • World population will increase 3 billion US population will increase 50 million Petroleum will be used up Sea level will rise 1-8+m Climate will warm several degrees Oceans will acidify Fishing will decrease Biodiversity & abundance will decrease enormously ONLY YOU CAN HELP YOUR CHILDREN, GRANDCHILDREN & YOURSELF What can you do for your Bay Area? NASA 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ? ? ? ? ? Thanks!! Jere H. Lipps [email protected]