* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Anatomy & Physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Exercise physiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Insect physiology wikipedia , lookup
Weight training wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Muscle contraction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
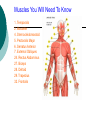
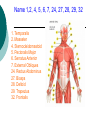
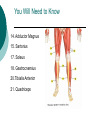
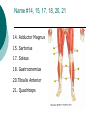
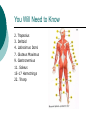
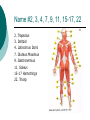
Congress Middle School Pre-Medical Magnet Program 2008 Presented by: Diana Herec, Medical Magnet Coordinator Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System Responsible for bodily movement Includes the voluntary muscles of the body About 700 muscles in the human body Vary greatly in size Muscle Action Muscle action depends on its position with the joint it works on Limb movement requires the teamwork of several muscles Muscles contract when activated Muscle Contraction If the force of a muscle contraction is greater than the force resisting it, the contraction is known as Isotonic Contraction muscle contraction continued… If resistance to contraction is equal to the force, the muscle will not contract, known as: Isometric Contraction Skeletal Muscle Most prominent type of muscle in the body May account for up to 60% body mass It is attached to bones at both ends by tendons Skeletal Muscle continued… Skeletal muscle is under constant control, therefore, known as: Voluntary Muscle Just below the surface of the skin The muscles and skeleton are responsible for an individual’s Physique Muscle Types Classified by shape: Parallel fibers Oblique fibers Shape and arrangement of fibers reflect muscle function Pennate Muscles Have feather-like appearance and fibers run obliquely down to the tendon Some spiral muscles have the capacity to turn half a rotation between their attachments Others twist around a bone In the common spindle-shaped muscles, all fibers run from one tendon to another Circular Muscles Fibers of circular muscles are arranged in concentric circles Muscles consist of bundles of fibers that can be organized in different ways, according to the function of the muscle Muscles You Will Need To Know 1. Temporalis 2. Masseter 4. Sternocleidomastoid 5. Pectoralis Major 6. Serratus Anterior 7. External Obliques 24. Rectus Abdominus 27. Biceps 28. Deltoid 29. Trapezius 32. Frontalis Name 1,2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 24, 27, 28, 29, 32 1. Temporalis 2. Masseter 4. Sternocleidomastoid 5. Pectoralis Major 6. Serratus Anterior 7. External Obliques 24. Rectus Abdominus 27. Biceps 28. Deltoid 29. Trapezius 32. Frontalis You Will Need to Know 14. Adductor Magnus 15. Sartorius 17. Soleus 18. Gastrocnemius 20.Tibialis Anterior 21. Quadriceps Name #14, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21 14. Adductor Magnus 15. Sartorius 17. Soleus 18. Gastrocnemius 20.Tibialis Anterior 21. Quadriceps You Will Need to Know 2. Trapezius 3. Deltoid 4. Latissimus Dorsi 7. Gluteus Maximus 9. Gastronemius 11. Soleus 15-17 Hamstrings 22. Tricep Name #2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 11, 15-17, 22 2. Trapezius 3. Deltoid 4. Latissimus Dorsi 7. Gluteus Maximus 9. Gastronemius 11. Soleus 15-17 Hamstrings 22. Tricep