* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Oceanography - pams
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
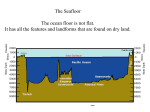
Oceanography cont. Oceanography Basic Facts… • The five major oceans/depths are Atlantic (3.92km), Indian (3.96km), Pacific (4.0km), Arctic (1.2km) and Southern (5.0km). • A sea is part of an ocean that is nearly surrounded by land. • Seven Seas are all considered part of a global ocean. Ocean Water • Ocean water consists of ALLthe natural elements found on Earth however is 96% pure water. • Scientists that study the ocean are called oceanographers. • Oceanography is the study of the composition of the water, temperature/life zones, and tide/wave interactions. Oceanography pt 2 The 3 Temperature Zones • These do not exist at the polar regions. • Surface zone – the zone where the water is mixed by waves and currents; fairly warm (100-400 meters down) More on zones… • Thermocline –a zone of rapid temperature change. Does not occur at a specific depth. • Thermo – means heat • Cline – means change in Last zone… • The deep zone – an area of extremely cold water that extends from the bottom of the thermocline to depths of 4000 m or more. At great depths the water is about 4 degrees Celsius. This is the biggest zone. Oceanography pt. 3 The Ocean Floor Draw this diagram and label in your notes. Features of the ocean floor… • Shoreline – the area where the land and the ocean meet. Does not mark the end of the continent. • A continental margin consists of a continental shelf, a continental slope, and a continental rise. Continental margin… • The shelf is the relatively flat part that is covered by shallow ocean water and is where the best fishing areas are found. At the edge of the shelf the ocean floor plunges steeply 4 to 5 km. This is the continental slope. Exploring Ocean Depths Continued… • Where the crust of the continent and the crust of the ocean floor meet is called the continental rise. Sediments at bottom are carried by turbidity currents, like an underwater avalanche. Turbidity current demo… More Features… • Submarine canyons – deep, v-shaped valleys cut in rock. One is actually deeper than the Grand Canyon (Monterey Submarine Canyon) Welcome to the Ocean Floor Ocean Floor landforms… • Abyssal plains – the flat ocean floor and consists of mud, sand, and silt close to the continents. Farther out is covered with remains of tiny organisms forming ooze. More… • Seamounts–are volcanic mountains. Over 1000 have been discovered. Some reach above the ocean to form an island Ex: Hawaii. • A guyot is a seamount with a flat top (underwater plateau) Life near the bottom Yep…still more landforms… • Trenches – the deepest part of the ocean found along the edges of the ocean floor next to the continents. The Marianas Trench is the deepest spot on the Earth. (more than 11,000 meters deep) Trench Ocean Floor Landforms Reefs • Reef – the limestone structures that contain the shells of animals. They surround islands offshore. • Fringing Reef – coral reefs that touch the shoreline of a volcanic island. Reef Habitats More types of reefs… • Barrier reefs – coral reefs that are separated from the shore by an area of shallow water called a lagoon. • Atoll – coral reef that surrounds an island that has been worn away and sunk beneath the surface. Barrier reefs and Atolls Tides • Tides are caused by gravitational pull between the sun, earth, and moon. • Spring tide – the highest high tide • Neap tide – the weakest high tide Exploring the Ocean Bio telemetry Sonar AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) ROV (Remotely Operated Vehicle) Upwelling Ocean Great Discoveries