* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacterial Cell Structure (continued)
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
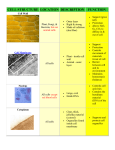
1 Ways to think about peptidoglycan 2 Bacterial Cell Structure (continued) You are here. Gram negative cell wall 3 Outer membrane • Lipid bilayer membrane: Asymmetric – Inner and outer leaflets • Inner leaflet made of phospholipids; outer leaflet is made of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) • LPS = endotoxin – Proteins for transport of substances • Porins: tri-subunit, transmembrane proteins – Barrier to diffusion of various substances • Lipoprotein: anchors outer membrane to PG 4 5 Structure of LPS extends from cell surface. contains odd sugars e.g. KDO. Gln-P and fatty acids take the place of phospholipids. www.med.sc.edu:85/fox/ cell_envelope.htm Periplasmic Space www.arches.uga.edu/~emilyd/ theory.html 6 7 Periplasm • The periplasm is the “stuff” in that space, – A hydrated gel including the PG – Binding proteins that aid in transport – Hydrolytic enzymes for breaking down large molecules – Chemoreceptor proteins that help direct swimming – Enzymes for synthesizing PG, OM • Must be in Gram + bacteria also. Glycocalyx: capsules and slime layers “Sugar covering”: capsules are firmly attached, slime layers are loose. Multiple advantages to cells: prevent dehydration absorb nutrients cell capsule protection from predators, WBCs protection from biocides (as part of biofilms) attachment to surfaces and site of attachment by others. www.activatedsludge.info/ resources/visbulk.asp 8 9 Non-Carbohydrate layers • S Layers – Crystalline, protein layers – Found widely in Archaea, also in G- and G+ • Polypeptide capsule – B. anthracis has a poly D-glutamic acid capsule TEM image of a freeze-etching preparation of a bacterial cell exhibiting an S-layer with square (p4) lattice symmetry. Bar, 100nm http://www.nano.boku.ac.at/1143.html?&L=1 Fimbriae and pili Both are appendages made of protein Singular: fimbria, pilus Both used for attachment Fimbriae: to surfaces (incl. host cells) and other bacteria. Pili: to other bacteria for exchanging DNA (“sex”). www.ncl.ac.uk/dental/oralbiol/ oralenv/images/sex1.jpg 10 11 Fimbriae and pili-2 http://www.mansfield.ohio-state.edu/~sabedon/006pili.gif Flagella 12 •Flagella: protein appendages for swimming through liquid or across wet surfaces. •Rotate like propellers. •Different from eukaryotic flagella. Arrangements on cells: polar, Lophotrichous, amphitrichous, peritrichous. www.ai.mit.edu/people/ tk/ce/flagella-s.gif www.bmb.leeds.ac.uk/.../icu8/ introduction/bacteria.html From the membrane in: the bacterial cytoplasm 13 • Cytoplasm is a gel made of water, salts, LMW molecules, and lots of proteins. • DNA = nucleoid, w/ proteins • Plasmids = small circular DNA • Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis. Cytoplasm may also contain inclusions, gas vacuoles, extended membrane systems, or magnetosomes. But generally NO membrane-bound organelles. 14 Inclusions and granules • Storage molecules found as small bodies within cytoplasm. • Can be organic (e.g. PHB or glycogen) or inorganic (Sulfur, polyphosphate. – PHB, a type of PHA, degradable plastic (polyester); glycogen, a polymer of glucose. – Sulfur, a metabolic byproduct; polyphosphate, polymer of PO4 http://www.accessexcellence.org/WN/SUA12/marg499.html 15 Magnetosomes Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum “Membrane”- coated pieces of magnetite, assist bacteria in moving to microaerophilic environments. An organelle? North is down. www.calpoly.edu/~rfrankel/ mtbphoto.html http://geoweb.tamu.edu/courses/geol101/lab/topo_maps/IMG00006.GIF