* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.4.08 105K lecture
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
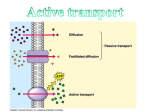
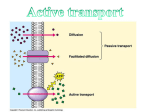
BIO105K tutoring Thursdays 1:00 – 2:00 in the Fish Bowl = room 153 Science Building Sam Giles M W Day Date 1/14 1/16 Subject To be read prior to this class period: no class - Snow Day! Evolution: Unity and Diversity Chapter 1 M W 1/21 1/23 no class – Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr. Day Water and the Chemical Environment Chapter 2 (except pp30-35) M 1/28 Quiz #1 on Ch. 1 and parts of Ch. 2 and related lectures/handouts (no make ups for missed quiz) Cell Membranes Chapter 6 W M 1/30 2/4 Macromolecules Macromolecules W 2/6 Quiz #2 on Ch. 3 and 6 and related lectures/handouts (no make ups for missed quiz) The Cell Chapter 7 M W M W M 2/11 2/13 2/18 2/20 2/25 Bioenergetics Cell Respiration no class - Winter Break no class - Winter Break EXAM I Chapter 3 (except pp63-69) Chapter 9 Chapters 1, 6,7, parts of 2, 3 Aquaporin protein makes a water channel through the cell (plasma) membrane. The function of Aquaporin is to allow the passive diffusion of water across the cell membrane. The structure of Aquaporin is a donut and water goes through the donut hole. Aquaporin increases the rate of osmosis. Chapter 3 is about protein structure and function. In Chapter 3, the material on pages 63 -69 is not really covered until after the first test. That means you need to read it now but you don’t need to study it until after the first test. Also, I will talk about this material in class but not until after the first test. The example will we use is the protein Aquaporin. Major Sites of Expression and Function of Human Aquaporin Aquaporin-0 Eye: lens fiber cells Fluid balance within the lens Aquaporin-1 Red blood cells Osmotic protection Kidney: proximal tubule Concentration of urine Eye: ciliary epithelium Production of aqueous humor Brain: choriod plexus Production of cerebrospinal fluid Lung: alveolar epithelial cells Alveolar hydration state Aquaporin-2 Kidney: collecting ducts Mediates antidiuretic hormone activity Aquaporin-3 Kidney: collecting ducts Reabsorbtion of water into blood Trachea: epithelial cells Secretion of water into trachea Aquaporin-4 Kidney: collecting ducts Reabsorbtion of water Brain: ependymal cells CSF fluid balance Brain: hypothalamus Osmosensing function? Lung: bronchial epithelium Bronchial fluid secretion Aquaporin-5 Salivary glands Production of saliva Lacrimal glands Production of tears Aquaporin-6 Kidney Very low water permiability; function? Aquaporin-7 Testis and sperm Aquaporin-8 Testis, pancreas, liver, others Aquaporin-9 Leukocytes Aquaporin creates a channel through the cell membrane that only lets H 2O through. membrane traffic in cells Some examples of endocytosis and exocytosis: 1) Aquaporin-2 in human kidney cells 2) neurotransmitter vesicles in all human nerve cells 3) phagocytosis of bacteria by human white blood cells 4) receptor-mediated endocytosis and cholesterol traffic in humans membrane traffic in cells Some examples of endocytosis and exocytosis: 1) Aquaporin-2 in human kidney cells 2) neurotransmitter vesicles in all human nerve cells 3) phagocytosis of bacteria by human white blood cells 4) receptor-mediated endocytosis and cholesterol traffic in humans membrane traffic in cells Some examples of endocytosis and exocytosis: 1) Aquaporin-2 in human kidney cells 2) neurotransmitter vesicles in all human nerve cells 3) phagocytosis of bacteria by human white blood cells 4) receptor-mediated endocytosis and cholesterol traffic in humans membrane traffic in cells Some examples of endocytosis and exocytosis: 1) Aquaporin-2 in human kidney cells 2) neurotransmitter vesicles in all human nerve cells 3) phagocytosis of bacteria by human white blood cells 4) receptor-mediated endocytosis and cholesterol traffic in humans Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) belongs to the lipoprotein particle family. Diameter is about 22 nm, Mass is about 3 million Daltons (one Hydrogen atom = 1 Dalton) But vary in size (A few large LDL are healthier than many small LDL.) Each LDL contain: 1) one B-100 protein molecule (It’s big: 4536 amino acid residues) B-100 binds to the LDL receptor on cells. 2) a highly-hydrophobic core consisting of linoleate, a fatty acid, and about 1500 cholestrol molecules 3) surrounded by a shell of phospholipids