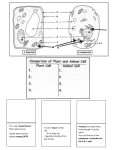
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Degradomics wikipedia , lookup
Enzymes: Regulatory Regulatory enzymes In a metabolic pathway, which utilizes numerous enzymes, a regulatory enzyme sets the rate of the overall sequence because it catalyzes the slowest, rate-limiting reaction Characteristics of regulatory enzymes 1. Allosteric control 2. Use of binding proteins 3. Reversible covalent modifications Proteins kinases and phophatases 4. Proteolytic activation Enzymes: Regulatory - Allosteric enzyme Allosteric enzymes Involve reversible noncovalent binding of regulatory compounds called allosteric modulators Binding of modulators can be inhibitory or stimulatory Binding of modulator causes conformational changes catalytic regulatory Enzymes: Regulatory - Allosteric enzyme Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) Feedback control by production of end product of pathway Allosteric inhibition - CTP inhibits aspartate transcarbamoylase by binding to a regulatory site (not an active site) Enzymes: Regulatory - Binding proteins Trypsin can be bound by trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) and inactivated Protease inhibitors are common in nature ~10% of blood plasma proteins are protease inhibitors A mutant of one protease inhibitor causes emphysema Enzymes: Regulatory - Reversible covalent modification Enzymes: Regulatory - Reversible covalent modification Methylation - involved in chemotaxis in bacteria ADP-ribosylation -involved in bacterial nitrogen fixation Examples: Diphtheria toxin and cholera toxin D toxin acts on and inhibits EF-2 (protein biosynthesis) C toxin acts on signaling protein (loss of body fluids - death) Phosphorylation - 1/3 to 1/2 of all euk. proteins are phosphorylated Enzymes: Regulatory - proteolytic activation Zymogen - inactive precursor (proteases) many proteases activated this way, activation is irreversible Proproteins/proenzymes - inactive precursor (other proteins) procollagen blood clotting system