* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diapositiva 1
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
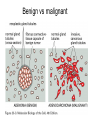
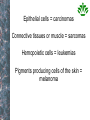
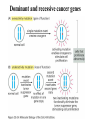
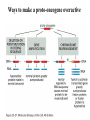
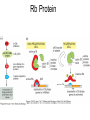
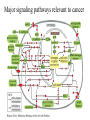
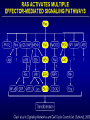
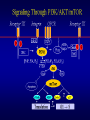
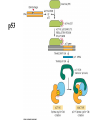
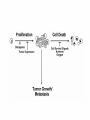
PROLIFERAZIONE CELLULARE E RESISTENZA AI FARMACI CANCER Cancer is characterized by abnormal, unrelated cell proliferation Cancer invades healthy tissues and compete with normal cells for oxygen, nutrients, and space Abnormal cells reproduce in the same way as normal cells, but they do not have the regulatory mechanisms to control growth The abnormal cell growth proliferates in an uncontrolled and unrestricted way. CANCER Tumors are also classified according to their cell of origin and whether their growth is benign or malignant BENIGN tumors remain at their site of origin They may grow large, but their growth rate is slower than that of malignant tumors They usually do not cause death unless their location impairs the function of a vital organ MALIGNANT tumors grow rapidly are likely to undergo metastasis (See table 20-2) Benign vs malignant Epithelial cells = carcinomas Connective tissues or muscle = sarcomas Hemopoietic cells = leukemias Pigments producing cells of the skin = melanoma 6 key behaviors of cancer cells 1. They disregard the external and internal signals that regulate cell proliferation 2. They are resistant to apoptosis 3. The avoid limitations to proliferation, such as differentiation and senescence 4. They are genetically unstable 5. They are invasive (escape home tissue) 6. The metastasize (survive and proliferate in foreign tissues) Clonal Evolution Genetic Instability and Tumor Progression Normal and deranged control of cell production from stem cells Dominant and recessive cancer genes Ways to make a proto-oncogene overactive The genetic mechanisms underlying retinoblastoma Rb Protein Major signaling pathways relevant to cancer p53 Telomerase is reactivated in Human cancers