* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis and Sex
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
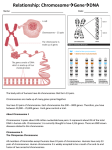
Meiosis and Sex-linked traits Ch. 10.4-10.5 Objectives 1. Explain chromosome theory of inheritance 2. Understand genetic linkage 3. Explain sex-linked genes and why more common in males Chromosome Theory of Inheritance • Mendel’s findings were not widely accepted at first • During the 1900’s, parallels discovered between genes and chromosomes • This is referred to as the chromosome theory of inheritance: • Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: – Genes located on chromosomes – accounts for inheritance patterns Chromosome Theory of Inheritance • Remember, diploid individuals have 2 sets of homologous chromosomes – One from mom, one from dad • Gene locus: – Alleles of a gene reside at same location Genetic Linkage and Crossing Over • Genetic Linkage: – Tendency for alleles on one chromosome to be inherited together • Closer the genes, the greater the genetic linkage • Farther apart, greater chance of separation Sex Linked Genes • What two sex chromosomes make up a male? Female? – Male = XY, Female = XX • Which chromosome is physically larger? – The X. It can hold a lot more genetic info • Sex linked gene: – Any gene on a sex chromosome Sex-linked Disorders • Many sex-linked disorders are recessive alleles – Let’s say that white eyes in fruit fly is an example • Disorders always carried on X chromosome (Y doesn’t have any room, too small) • What does all this mean? Sex-linked Disorders • If disease is recessive and always carried on X chromosome, then females (XX), will most likely have dominant form of allele on other chromosome --> don’t get disorder. • If males (XY) have allele for disorder on their X chromosome, they will get disorder because Y chromosome doesn’t carry alleles. Rare!