* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biotechnology2
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
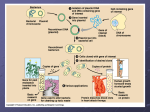
Biotechnology AP Biology 2007-2008 D.N.A Review HW concept questions and be ready to ask any questions that you may have Take 15 minutes to COMPLETE building your protein synthesis poster AP Biology I will be coming around for you to discuss your poster with me A Brave New World AP Biology TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGGATGCCGCGACTATGATC ACATAGACATGCTGTCAGCTCTAGTAGACTAGCTGACT human genome CGACTAGCATGATCGATCAGCTACATGCTAGCACACYC GTACATCGATCCTGACATCGACCTGCTCGTACATGCTA 3.2 billion bases CTAGCTACTGACTCATGATCCAGATCACTGAAACCCTA GATCGGGTACCTATTACAGTACGATCATCCGATCAGAT CATGCTAGTACATCGATCGATACTGCTACTGATCTAGC TCAATCAAACTCTTTTTGCATCATGATACTAGACTAGC TGACTGATCATGACTCTGATCCCGTAGATCGGGTACCT ATTACAGTACGATCATCCGATCAGATCATGCTAGTACA TCGATCGATACTGCTACTGATCTAGCTCAATCAAACTC TTTTTGCATCATGATACTAGACTAGCTGACTGATCATG ACTCTGATCCCGTAGATCGGGTACCTATTACAGTACGA TCATCCGATCAGATCATGCTAGTACATCGATCGATACT AP Biology Biotechnology today Genetic Engineering manipulation of DNA if you are going to engineer DNA & genes & organisms, then you need a set of tools to work with this unit is a survey of those tools… AP Biology Our tool kit… Bacteria Bacteria review one-celled prokaryotes reproduce by mitosis binary fission rapid growth generation every ~20 minutes 108 (100 million) colony overnight! dominant form of life on Earth incredibly diverse AP Biology Transformation Bacteria are opportunists pick up naked foreign DNA wherever it may be hanging out have surface transport proteins that are specialized for the uptake of naked DNA mix heat-killed pathogenic & non-pathogenic bacteria import bits of chromosomes from other bacteria incorporate the DNA bits into their own chromosome express new genes transformation form of recombination AP Biology mice die Plasmids Small supplemental circles of DNA 5000 - 20,000 base pairs self-replicating carry extra genes 2-30 genes can be exchanged between bacteria bacterial sex!! rapid evolution can be imported from environment AP Biology How can plasmids help us? A way to get genes into bacteria easily insert new gene into plasmid insert plasmid into bacteria = vector bacteria now expresses new gene bacteria make new protein gene from other organism cut DNA plasmid AP Biology recombinant plasmid + vector glue DNA transformed bacteria Biotechnology Plasmids used to insert new genes into bacteria cut DNA gene we want like what? …insulin …HGH …lactase cut plasmid DNA Cut DNA? DNA scissors? ligase recombinant APplasmid Biology insert “gene we want” into plasmid... “glue” together How do we cut DNA? Restriction enzymes restriction endonucleases discovered in 1960s evolved in bacteria to cut up foreign DNA “restrict” the action of the attacking organism protection against viruses & other bacteria AP Biology cut DNA at specific sequences CTGAATTCCG restriction site produces protruding ends GACTTAAGGC Restriction enzymes Action of enzyme sticky ends CTG|AATTCCG will bind to any complementary DNA GACTTAA|GGC Many different enzymes named after organism they are found in EcoRI, HindIII, BamHI, SmaI AP Biology Restriction enzymes Cut DNA at specific sites leave “sticky ends” restriction enzyme cut site GTAACGAATTCACGCTT CATTGCTTAAGTGCGAA restriction enzyme cut site GTAACG AATTCACGCTT CATTGCTTAA GTGCGAA AP Biology Sticky ends Cut other DNA with same enzymes leave “sticky ends” on both can glue DNA together at “sticky ends” GTAACG AATTCACGCTT CATTGCTTAA GTGCGAA AP Biology gene you want GGACCTG AATTCCGGATA CCTGGACTTAA GGCCTAT chromosome want to add gene to GGACCTG AATTCACGCTT CCTGGACTTAA GTGCGAA combined DNA Sticky ends help glue genes together cut sites gene you want cut sites TTGTAACGAATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCGAATTCACGCTT AACATTGCTTAAGATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAAGTGCGAA AATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCG GATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAA sticky ends cut sites isolated gene chromosome want to add gene to AATGGTTACTTGTAACG AATTCTACGATCGCCGATTCAACGCTT TTACCAATGAACATTGCTTAA GATGCTAGCGGCTAAGTTGCGAA DNA ligase joins the strands sticky ends stick together Recombinant DNA molecule chromosome with new gene added TAACGAATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCGAATTCTACGATC AP Biology CATTGCTTAAGATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAAGATGCTAGC How can bacteria read human DNA? Why mix genes together? Gene produces protein in different organism or different individual human insulin gene in bacteria TAACGAATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCGAATTCTACGATC CATTGCTTAAGATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAAGATGCTAGC “new” protein from organism ex: human insulin from bacteria aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa bacteria AP Biology human insulin Transforming Bacteria The gene for HGH (growth hormone) is removed from a human cell AP Biology Plasmid The plasmid is cut at certain sequences in the DNA using the same Restriction Enzyme used to cut the HGH gene from a human cell The plasmid will have sticky ends in addition to the HGH gene AP Biology The gene for HGH is then mixed with the bacterial plasmid, and the HGH is incorporated into the plasmid DNA Ligase covalently bond the sugar phosphate backbone The plasmid is then added to the bacteria AP Biology The bacteria now has the gene for HGH, and has the ability to produce it This shows the process of transformation in bacteria AP Biology The code is universal Since all living organisms… AP Biology use the same DNA use the same code book read their genes the same way Copy (& Read) DNA Transformation insert recombinant plasmid into bacteria grow recombinant bacteria in agar cultures bacteria make lots of copies of plasmid “cloning” the plasmid production of many copies of inserted gene production of “new” protein transformed phenotype DNA RNA protein trait AP Biology Green with envy?? Jelly fish “GFP” AP Biology Transformed vertebrates HW: Read 12.10-12.15 Complete Recombinant (Plasmid) DNA questions AP Biology AP Biology Cut, Paste, Copy, Find… Word processing metaphor… cut restriction enzymes paste ligase copy plasmids bacterial transformation is there an easier way?? find ???? AP Biology D.N.A Objective: SWBAT examine the arguments supporting and opposing the use of Golden Rice and evaluate the merits of using GMO’s in society. Explain how DNA segments can be cut and spliced together to produce recombinant DNA. How do the segments “find” each other and stick together? How is recombinant DNA then cloned to produce multiple copies of the gene? AP Biology A restriction enzyme is used to cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence It cuts the two strands of DNA, forming “sticky ends” – can easily hydrogen bond to other DNA strands Enzyme DNA ligase links pieces of DNA A fragment of DNA can be spliced into a plasmid (circular bacterial DNA) Transformation – bacteria can take up the plasmid and begin to replicate the newly DNA sequence AP Biology GOLDEN RICE DEBATE Ethical Question: Should Golden Rice be used in developing nations to combat vitamin A deficiency AP Biology STEP 1: RESEARCH GET INTO TEAMS OF 4 SOME TEAMS WILL RESEARCH PRO, OTHER CONS MAKE SURE YOU TAKE NOTES YOU WILL NOT BE ABLE TO USE YOUR RESEARCH PAPER (1O MIN) STEP 2: CONVINCE OTHERS OF YOUR POSITION CREATE A MINI TEAM (2) WITHIN YOUR GROUP OF 4 COMBINE WITH ANOTHER MINI TEAM AND PREPARE YOUR ARGUMENT (5 MIN FOR PRO, 5 MIN FOR CON) STEP 3: CONVINCE OTHERS OF THE OPPOSING POSITION FIND A MINI TEAM THAT HAD AN OPPOSING VIEW NOW YOU MUST ARGUE FOR THAT OPPOSING VIEW (5 MIN CON, 5 MIN PRO) AP Biology AP Biology