* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15: Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
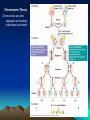
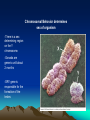
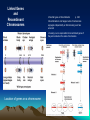
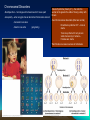
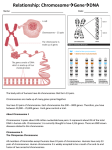
Chapter 15: Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance (Link between Meiosis or cellular processes and Genetics) Objectives 1. Mendelian Genetics is based on the physical behavior of chromosomes 2. Sex linked genes have unique inheritance patterns 3. Linked genes are often inherited together due to physical proximity on the chromosome 4. Alterations of chromosome number or structure results in genetic disorders 5. There are some exceptions to the inheritance patterns Chromosome Theory Chromosomes are what segregates and undergo independent assortment. Chromosomal Behavior determines sex of organism -There is a sex determining region on the Y chromosome. -Gonads are generic until about 2 months -SRY gene is responsible for the formation of the testes Sex Linked Genes -Sex linked recessive genes for color blindness -homozygous recessive females have the trait -males that get the recessive allele from mom will have the disease X Chromosome Inactivation -One of the X chromosomes in females becomes in active. -Barr Bodies are the inactive version of the X chromosome -Inactivation doesn’t happen right away -Females that are heterozygous for a certain X chromosome trait can express both traits during development. -Inactive versions produce the same in active versions during mitosis. Linked Genes and Recombinant Chromosomes -Parental types vs Recombinants p. 294 -Recombinations can happen when chromosomes segregate indpendently or after crossing over has occurred -Crossing over is responsible for recombinant genes if they are located on the same chromosome Location of genes on a chromosome Chromosomal Dissorders -Nondisjunction – homologous chromosomes don’t move apart -Aneuploidy – when a zygote has an abnormal chromosome amount -Sex Chromosomes dissorders (Most are normal) -monosomic one less -trisomic one extra -Downs Syndrome (trisomy 21) – the older the woman is the greater the odds of having a baby with Downs (polyploidy) Klinefelters syndrome XXY – male is sterile Turnner syndrome XO only known viable monosomy in humans – Females are sterile *Barr Bodies are reason success of individuals Alterations of Chromosome Structures *Many cases cause severe problems – most don’t make it to birth