* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Heredity - Catawba County Schools
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
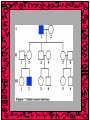
Human Heredity Ch 14 Human Chromosomes • Karyotype – picture of chromosomes grouped together in pairs • 23 pairs (46 total) • Two are sex chromosomes (pair #23) – Female genotype – XX – Male genotype – XY • Autosomes – remaining 44 chromosomes – Pair #s 1-22 • Gender of zygote is determined by male Human Traits • Pedigree – chart that shows relationship in family • Used to infer genotypes of family members Recessive alleles • An abnormal gene shows up when an abnormal allele affects the phenotype • Recessive – only shows up when _________ Dominant allele • Expressed even if recessive allele present Sex-linked genes • Only Genes located on X and Y chromosomes • X chromosome contains more genes being larger • Y chromosome is small so can’t carry other traits besides the one determining the male sex characteristics • Males MUST always express all of their X genes • ** You can tell a trait is sex-linked if more males than females have it in the population!!** Chromosomal disorders • Errors in meiosis • Nondisjunction - Homologous chromosomes fail to separate • Abnormal numbers of chromosomes in gametes Sex chromosome disorders • Disorders in the sex chromosomes • May only have one X – Sterile, sex organs do not develop at puberty • Or be a male with two X • Presence of Y chromosome produces male sexual development no matter how many X • Lack of Y, the embryo develops as a female • http://www.zerobio.com/drag_gr11 /sexlink.htm