* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction and Heredity
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
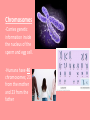
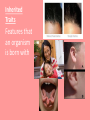
Reproduction and Heredity Sexual Reproduction • The process in which new offspring are produced by two parents Asexual Reproduction -Some organisms produce offspring with only one parent -Offspring is an exact copy of parent with exact same genetic information -Some plants reproduce this way: spores (ferns) or buds (potatoes), and runners Asexual Reproduction • Cells divide in stages called MITOSIS - Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telephase Mitosis – phases of asexual reproduction Sexual Reproduction -When two parents join together to form a new individual -offspring will NOT be identical to one parent. -It will have traits from both parents -flowers, animals, and humans reproduce this way Sperm cell Contains male genetic information that will combine with female egg cell to produce a new “individual” Egg cell female cell that contains genetic information that will combine with the male sperm cell to produce offspring Chromosomes -Carries genetic information inside the nucleus of the sperm and egg cell. -Humans have 46 chromosomes; 23 from the mother and 23 from the father Fertilization When the egg and sperm cell come together to form a new individual Meiosis The process cell use to divide for SEXUAL reproduction First stage begins with 23 chromosomes from each parent, for a total of 46 Variation The differences between organisms of a species Gene Specific parts of a chromosome that are responsible for one trait in that offspring. For example: hair color, eye color in humans; the genes of a tree control the size, shape, and color of its leaves. Inherited Traits Features that an organism is born with Dominant Trait When gene from one parent overpowers the gene from the other parent Brown eyes, cleft chin, tongue-rolling are all dominant traits Other dominant traits • • • • • • Straight thumb and pinky Dimples Freckles Straight hair line Curly hair Detached earlobes Recessive Trait When gene from one parent is overpowered by the gene of the other parent Blue eyes, attached ear lobes, bent pinky/thumb are all recessive traits Dominant vs Recessive Dominant traits are more common than recessive traits Learned Behavior Skills that animals are taught during their lifetime by parents or other animals, and through experience. Inherited Behaviors/ Instincts Behavior that animals are born knowing; they are instinctual. Animals do not have to be taught an inherited behavior. nest and web building, migration, hibernation. Scientists’ Work • Gregor Mendel • Thomas Hunt Morgan Gregor Mendel • Studied tall and dwarf pea plants and what happens when you cross-breed them • Formulated 3 laws that became the basis of the science of heredity • Wrote a paper to describe his findings, but no one seemed to care about his work • Later, after his death, other scientists, who were working on the same ideas, discovered his important work. Thomas Hunt Morgan • American biologist • Discovered the role the chromosome plays in heredity • Demonstrated that genes are carried on chromosomes by researching and using fruit flies in an experiment