* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dark Blue with Orange
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
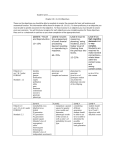
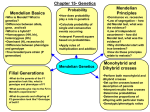
Fundamentals of Genetics (Ch.9.1 + 9.2) Genetics is the field of biology devoted to understanding how characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring. Objectives 1. Explain the significance of Mendel's experiments and observations, and the laws derived from them. 1.1 Explain the concept of independent events. 1.2 Understand that the probability of an independent event is not altered by the outcomes of previous events. 1.3 Describe Mendel's experiments and observations. 1.4 Describe the relationship between genotype and phenotype. 1.5 Use the concept of the gene to explain Mendel's laws. 1.6 Describe the ideas of dominant and recessive traits with examples. 1.7 Consider the value of the punnett square by creating examples of mono and dihybrid crosses. 1.8 Explain the law of segregation. THINK, PAIR UP, AND SHARE! Think, Pair, Share 2.10 Discuss the similarities and differences between sex chromosomes and somatic chromosomes. 2.11 Using examples from living organisms discuss the importance of asexual and sexual reproduction to their growth and survival. Independent Events If events happen independently of each other they... If events were to be dependent on each other they... Mendel the Monk Gregor Mendel was an Austrian Monk, who specialized in statistics. Heredity – transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring. Traits – a category in which alternate characteristics can be observed Mendel's Crosses and Results Mendel's Laws Law of Segregation – a pair of factors is segregated or separated during the formation of gametes. Law of Independent Assortment – factors for different characteristics are distributed to gametes independently. WHAT DO THESE MEAN EXACTLY? Genes and Alleles Gene is a segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a particular hereditary trait. Alleles are the different types of characteristics the gene can express. These alleles are represented by letters. G = capital means dominant g = lower case means recessive Genotype vs Phenotype Genotype – its “genetic type” or make-up Phenotype – its visible appearance – what we see Dominant – will reflect appearance regardless of the other trait's characteristics. Recessive – only will reflect appearance if paired with another recessive. Punnett Squares – Monohybrid and Dihybrid Crosses P Generation – 1 Parental F1 Generation – Fillial (offspring) Pure – breed only a specific trait Strain – plants that are pure for a specific trait Y = Dominant Yellow Genotypes: 2 Yy, 2 yy y = Recessive Green Phenotypes: 2 yellow, 2 green Dihybrid Cross R - round r – wrinkled Y – yellow y - green Homozygous vs Heterozygous Homozygous – allele is with the exact same allele as itself. Heterozygous – allele is paired with a different allele (characteristic). GG Gg Dominance Complete Dominance one allele “pwns” the other. You only see the one phenotype. Incomplete Dominance two or more alleles influence the phenotype. Codominance both alleles are expressed independently. Blonde (B) + brown (B') hair. Assignments + Practice Test Cross – if you know something expresses a certain phenotype, but want to know its genetype for a trait, cross is with a purebreed and observe the results! 9.1 9.2 Punnett Square Problems Objectives Achieved? 1. Explain the significance of Mendel's experiments and observations, and the laws derived from them. 1.1 Explain the concept of independent events. 1.2 Understand that the probability of an independent event is not altered by the outcomes of previous events. 1.3 Describe Mendel's experiments and observations. 1.4 Describe the relationship between genotype and phenotype. 1.5 Use the concept of the gene to explain Mendel's laws. 1.6 Describe the ideas of dominant and recessive traits with examples. 1.7 Consider the value of the punnett square by creating examples of mono and dihybrid crosses. 1.8 Explain the law of segregation.