* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2010 exams4u feedback to students
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
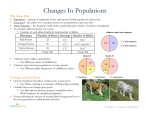
Level 2 Bio Genetics 2010 Feedback to students OVERALL • Very poor attempt by many students. • LOTS OF REVISION NEEDED! • Often you must answer all parts of a question correctly to gain the achieved grade for that question. OVERALL • Q1 generally completed well but without getting an achieved or higher in a question relating to gene pool you will not pass the external exam. You MUST show knowledge across all areas of the standard to pass (i.e. mendelian genetics AND population genetics) YOU MUST LEARN DEFINITIONS!!! • Writing just the names of the terms should be done only when the question states IDENTIFY or NAME. • DESCRIBE or DEFINE: means basically “give the definition for the key terms”. • N.B. If in doubt give the definition of the key words in the question. This is often all that is required for the Achieved grade. DEFINITIONS YOU MUST KNOW The following terms were often misused or incorrectly defined student exam answers: N.B. There are more in definitions that you should topic. • Allele know for this •genetics Gene pool However ones that were in the • Gene these are just the • Evolutionary process particular set of• questions used • Organism Genetic Drift in this school exam. • Species • Natural Selection • Population • Test cross • Community • Inbreeding QUESTION ONE Question ONE Achievement 4A or better Merit Excellence 2M and 2A 1E, 2M or better and 2A or better N.B. Each question was made up of parts. Each part was assigned a grade and these grades were then totalled for your overall grade for each question. QUESTION ONE a) Achievement Merit Excellence Duroc : bbww Hampshire : BBWW F1 : BbWw • Most answered correctly • Required genotype of parents – NOT their gametes therefore needed 2 B/b alleles AND 2 W/w alleles QUESTION ONE b) Achievement Pure breeding means that the individual has a homozygous geneotype / can produce only one type of allele Merit Excellence Homozygous parent can pass on only one type of allele (for that trait) to its offspring (there is NO variation in the alleles) so offspring have same alleles and phenotype as parent. • Again learn your definitions! • Many on the right track but what was written was not correct. • N.B. pure breeding is a term used to describe an individual – it is not the mating process! QUESTION ONE c) Achievement Gametes correct Merit Excellence Whole Punnet Square correct • Most did this well • If you did not get an M then you must get some help to get this right in the future. • There will definitely be a dihybrid cross to complete in the external. QUESTION ONE d) Achievement One of bbWW; bbWw Merit Both bbWW and bbWw and no other genotype given. • Many repeated bbWw Excellence QUESTION ONE e) Achievement Merit 3/16 or 3 : 15 or correct decimal (0.1875) or 18.75% • Most did this correctly Excellence QUESTION ONE f) Achievement Merit Excellence Gives genotype as bbWW and describes breeding suspect pigs with recessive genotype (bbww) pigs i.e. test cross AND check whether offspring have white bands or are solid red only. OR Good attempt at Punnet Squares with probabilities and linked in answer As for Achieved and explains that •Solid red offspring indicates suspect pig is bbWw; all white banded offspring indicates suspect pig (may be) bbWW. •if any offspring do not have white band / are solid red (bbww) then adult is heterozygous (bbWw) and not pure breeding for white banded offspring. As for Merit and includes explanation of the need for several breedings eg if no solid red (bbww) pigs occur in the large numbers of offspring, then the suspect pig is (almost certainly) bbWW so pure breeding. Answer supported with correct Punnet Squares of crosses (bbWw x bbww and bbWW x bbww) to show the probability of getting white banded and solid red offspring. • Many failed to identify that a TEST CROSS was required QUESTION ONE f) cont • Red is recessive therefore only appears when there is no B allele present. Punnet squares can therefore be simplified to monohybrid crosses of W/w alleles. • Many did not read the information provided to recognise the desired pure breeding phenotype for this question was red with a white band. QUESTION ONE f) cont • Many failed to mention that lots of crosses would be needed to make “almost certain” that the unknown individual was bbWW • Many did not say that if only one offspring of the test cross had recessive “no band” phenotype then the unknown parent was heterozygous so should be kulled as not pure breeding. QUESTION TWO Question TWO Achievement 2A or better Merit Excellence 1M for (c) 1E, 1M and 1A or and 1A better QUESTION TWO a) Achievement Merit Excellence Describes TWO of eg Mutation(s) in DNA creates new alleles. Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes produces genetically varied gametes. Crossing over and recombination between non sister chromatids in meiosis produces new allele combinations in gametes. OR both correctly identified and 1½ reasonable descriptions • DESCRIBE does NOT mean “only name” • A Mutation does NOT make a new GENE – it makes a new allele • Source = where it comes from QUESTION TWO b) Achievement Mutation with brief description of how it shows in individual or in gene pool OR Migration with correct description (as question states gene pool – not species) Merit Excellence Mutation must occur in gamete producing cells [not somatic cells] for it to enter gene pool. If the gamete with the mutation is fertilized and the offspring produced is viable, then the mutation will enter the gene pool of the population. • Question was flawed as a) was regarding a species and b) was regarding a gene pool hence alteration in italics above. QUESTION TWO c) Achievement Describes Natural selection as causing : •mutations that are helpful / favourable to become established in the gene pool / produce more offspring OR •mutations that are helpful / unfavourable to not become established in the gene pool OR •Correct definitions of NS and links to gene pool e.g. increase in allele frequency of favourable alleles (or vise versa for unfavourable alleles) Merit Explains ONE of ; •Selection pressures will cause individuals with favourable alleles to survive and reproduce (increased fitness) so establishing and increasing the frequency of these alleles in the gene pool. •Selection pressures will cause individuals with unfavourable alleles to not survive / have reduced chance of surviving (reduced fitness) so these alleles will not get established in the gene pool or be present in low frequencies in the gene pool Excellence Discussion explains the role of NS in determining the presence of both favourable and unfavourable alleles in the gene pool linked into a comprehensive answer • NS acts on PHENOTYPE (NOT genotype/allele/gene). This leads to increase/decrease of the ALLELES for that phenotype in the next generation QUESTION TWO c) cont • Most answers lacked link to gene pool • NS is NOT mate selection • NS still occurs even in a stable (i.e. non-changing) environment QUESTION THREE Question THREE Achievement 2A or 1M or better Merit Excellence 1M and 1E, and 1A 1A or better QUESTION THREE a) Achievement Merit Excellence Any three with correct (or reasonable attempts at) descriptions for each of : Bottleneck effect Founder effect Genetic drift Mutation Natural selection • Majority of students did not know what an evolutionary process was. • Many did not read the question so did not give three processes or only named them and did not give a description. QUESTION THREE a) cont Descriptions for this example include: • Bottleneck effect – eg numbers of robins were greatly reduced so likely loss / reduction in allele frequency with likely a reduction in genetic diversity. QUESTION THREE a) cont • Founder effect – eg only 6 breeding pairs introduced to Ulva so alleles present in their gene pool not liely to be representative of the mainland / ancestral population so likely reduced genetic diversity. QUESTION THREE a) cont • Genetic drift – loss / reduction in specific alleles due to chance which is likely to be more pronounced in the small robin population so corresponding [increased] loss of genetic diversity. • Mutation – changes to genetic code creating new alleles. If occurring in gamete producing cells will enter gene pool as inherited. QUESTION THREE a) cont • Natural selection – changes in the environment cause change in selection pressures on robins so favourable alleles will be selected for and increase in frequency in gene pool. QUESTION THREE b) Achievement Merit Excellence Describes inbreeding eg • the breeding of closely related individuals eg siblings, children to parents; grand children to grandparents in the robin population. and its effect on one evolutionary process eg •Inbreeding in the small robin population is likely to further reduce the genetic diversity of the population that has occurred in bottleneck effect / founder effect / genetic drift •Mutations that are favourable will become established / increase in frequency in the gene pool more rapidly with inbreeding. •Favourable alleles selected for in NS will increase in frequency more rapidly with inbreeding. Or gives a comprehensive explanation of inbreeding (as per merit column) Explains inbreeding eg •The small size of the population increases the occurrence of inbreeding occurring by chance so that the degree of relatedness between all members of the population is high. This increases the chances of harmful recessive alleles coming together in any individual so reducing its fitness. and explains its effect on one evolutionary process eg •Inbreeding will reduce the genetic diversity of the small population that has already occurred in bottleneck effect / founder effect / genetic drift as the breeding of closely related individuals increases the chances of the loss of alleles from the gene pool. •Closely related individuals have alleles in common. A mutation that creates a new allele will be more common in related individuals. Inbreeding will therefore increase the chances of a mutation spreading through the population and so becoming established / increasing in frequency in small gene pool. •Favourable alleles are selected for so increases in frequency in the gene pool. Inbreeding will increase the spread of these favourable alleles through the small gene pool so further increasing their frequency. Explains inbreeding and its effect on three evolutionary processes linked to the decrease of diversity in the gene pool and the rapid increase in frequency of favourable alleles in the gene pool. QUESTION THREE b) cont • Definition of inbreeding often too basic or poorly worded. Many did not recognise that the main problem with inbreeding is that it increases the chances of (harmful) recessive alleles coming together in offspring and being expressed thus reducing the fitness of the individual. • Others, because of lack of recall on evolutionary processes, failed to achieve second part of question. QUESTION ONE • Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Vivamus et magna. Fusce sed sem sed magna suscipit egestas. • Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Vivamus et magna. Fusce sed sem sed magna suscipit egestas. JUDGEMENT STATEMENT Achievement Achievement with Merit Two questions answered correctly. Minimum of 2 x A. All questions answered correctly including TWO at Merit level. Minimum 2 x M + 1 xA Achievement with Excellence All questions answered correctly including TWO at Excellence level. Minimum 2 x E + 1 xA REMEMBER: • READ THE INFORMATION PROVIDED • READ THE QUESTION – underline the key terms • ATTEMPT ALL PARTS OF ALL QUESTIONS! If you are not sure then simply put the definitions of the key terms. QUESTION ONE Achievement Two questions answered correctly. Minimum of 2 x A. Achievement with Merit All questions answered correctly including TWO at Merit level. Minimum 2 x M + 1 x A Achievement with Excellence All questions answered correctly including TWO at Excellence level. Minimum 2 x E + 1 x A