* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap. 13 Sex Linked Inheiritance_2
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
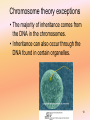
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis–Inheritance Connection Chapter 13 History of Inheritance • Carl Correns – 1900 – First suggests central role for chromosomes • Walter Sutton – 1902 – Chromosomal theory of inheritance • Carl Correns – 1909 – Suggests link between heredity and sex • Thomas Morgan – Fruit flies 2 • T.H. Morgan – 1910 – Working with fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster – Discovered a mutant male fly with white eyes – Wanted to see if this trait was inheritable 3 Parental Generation 4 F1 Cross 5 Testcross 6 Sex-Linked Traits • Sex chromosomes: – “The two chromosomes associated with an organism’s determination of male or female”. • Sex chromosomes vary according to species • Drosophila sex is based on the number of X chromosomes • • 2 X chromosomes = female 1 X and 1 Y chromosome = male • Sex-linked trait • “A trait determined by a gene on a sex chromosome” 7 X chromosome Y chromosome Human Chromosomes 8 Dosage compensation • It would seem that since a female has two X chromosomes, she should create twice as many proteins as a male who has only one causing another set of problems. But this doesn’t happen. Why? • Dosage compensation 9 Chromosome theory exceptions • The majority of inheritance comes from the DNA in the chromosomes. • Inheritance can also occur through the DNA found in certain organelles. 10 Genomic imprinting • “Phenotype exhibited by a particular allele depends on which parent contributed the allele to the offspring” 11 Nondisjunction of Autosomes • “Failure of homologues or sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis” • Aneuploidy – gain or loss of a chromosome – Monosomy – loss of a chromosome – Trisomy – gain of a chromosome 12 13 Trisomy 18 14 Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes • The result of nondisjunction of sex chromosomes is different than nondisjunction of autososomes. 15