* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendel`s Peas
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
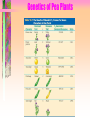
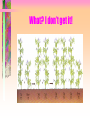
Mendel’s Peas pg. 648 • Describe Mendel’s genetics experiments • Identify the factors that control the inheritance of traits in organisms • Explain how genetics use symbols to represent alleles Vocabulary • • • • • • • • • Hereditypurebredgenealleledominant allelerecessive allelehybridGeneticsTraits- Questions: 1. What factors control the inheritance of traits in organisms? 2. What is a purebred? 3. If a pea plant has a tall stem, what possible combinations of alleles could it have? Gregory Mendel 1851 Priest, Teacher, Gardner • Pea plants have different traits - different physical characteristics • similar to parentsheredity - passing of traits from parents to offspring) • 10 yrs. of study & 1000’s of plants to understand heredity • his work laid foundation for genetics-study of heredity Flowering Pea Plant • traits in only two forms • produce many offspring • able to collect much data • developed method of cross pollinating Genetics of Pea Plants Mendel’s Experiments -wanted to cross tall with short purebred plants - always produce the same form of trait as the parent • Tall purebred • Short purebred • Tall offspring • Short offspring -self pollinate for many generations -offspring will always be identical to parent Experiment #1 • Tall Purebred • parental generation=P X • Short Purebred • parental generation=P F1 generation filial “son” in latin Surprise! • F1 generation-------- All Tall • short trait disappeared ? • Next, let grow and let self pollinate Surprise again!!! F2 (second filial generation) • Mix of tall and short • no F1’s were short; shortness trait reappeared What? I don’t get it! Inferences made by Mendel • Individual factors control inheritance of traits • Factors controlling traits exist in pairs; male and female • One factor can ‘mask’ (hide) another, example: Tall masked short height • Scientists call factors that control traits, ‘genes’. • Different form of genes are alleles. ‘Gene’ that controls ‘Stem Height’ alleles • T • s • T • T • s • s Combination of two Dominant allele (Capitalized) -always shows up in organism when present Recessive allele (lower case) -masked or covered up when dominant allele is present Understanding Mendels Crosses • 1 tall allele ‘ D’ • 1 short allele ‘ r’ TT TT TT Ts • 1 tall, 1 short =hybrid-two different TT TT Ts ss alleles for the trait Mendel’s Contribution • 1866 submitted paper to Scientific Society; other scientists deemed not important, too oversimplified • no phones or communication • forgotten for 34 years • 1900 three other scientists came upon same conclusion and recognize Mendels’ work • Father of Genetics Mendel quiz 1. Different forms of a gene. 2. An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present 3. An organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent 4. An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present. 5. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. 6. A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. 7. An organism that has two different alleles for a trait. Questions: 8. What factors control the inheritance of traits in organisms? 9 & 10. If a pea plant has a tall stem, what possible combinations of alleles could it have? Answers to Mendel quiz 1 pt. each 1. Allele 2. Recessive allele 3. Purebred 4. Dominant allele 5. Heredity 6. Gene 7. Hybrid 8. Genes 9 & 10. TT, Ts. __/10