* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ENVI 30 Environmental Issues
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
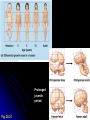
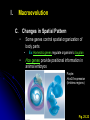
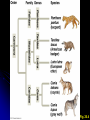
I. Macroevolution • Major innovations separation at higher taxonomic levels Exaptation A. • Existing feature modified to perform novel function • • • Some plasticity in biological structures Ex: Bird feathers evolved from reptile scales • • • • Ex: Development of bird wings from reptiles forelimbs not designed for flight May have provided insulation for primitive birds Preadaptation for flight Ex: Middle ear bones in mammals evolved from jaw bones in reptiles Does not imply that structures developed in anticipation of future use I. Macroevolution B. Developmental Rate and Timing • • • • Some evolutionary modifications result from minor genetic changes Heterochrony May affect regulatory genes Ex: Allometric growth – Changes in relative growth rates of body parts during development Prolonged juvenile period Fig. 25.21 I. Macroevolution B. Developmental Rate and Timing • Paedomorphosis – Retention of juvenile characteristics in adults Fig. 25.22 I. Macroevolution C. Changes in Spatial Pattern • Some genes control spatial organization of body parts • • Ex: Homeotic genes regulate organism’s bauplan Hox genes provide positional information in animal embryos Purple: HoxC6 expression (limbless regions) Fig. 25.23 I. Macroevolution C. Changes in Spatial Pattern • Regulatory changes may affect gene expression without changes in gene sequence Fig. 25.25 I. Macroevolution D. Directionality • Macroevolution not goal-oriented Fig. 25.27 II. Phylogeny and Systematics • • • Evolutionary processes reflected in organismal phylogeny Genealogies often represented as phylogenetic trees that reflect relationships among species Systematics deals with classification of taxa according to evolutionary history Fig. 26.4