* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
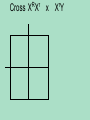
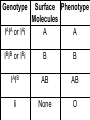
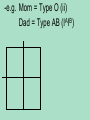
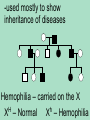
The patterns of heredity discovered by Mendel are called simple Mendelian inheritance or simple dominant/ recessive -because only 2 options for phenotypes & 2 alleles Non-Mendelian Inheritance 1. Incomplete dominance: -phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate to that of the homozygous parents e.g. flowers Red x White = Pink RR x R1R1 = RR1 2. Codominance (codominant alleles) -phenotypes of both homozygote parents are expressed in the heterozygote e.g. flowers Purple x White = Purple&White PP x WW = PW 3. Polygenic inheritance: -trait is controlled by 2 or more genes -produces multiple phenotypes e.g. Skin color = 3 genes(6 alleles) AaBbCc 4. Sex-linked traits: -traits are controlled by genes found on the sex chromosomes rd -sex chromosomes: the 23 pair in humans, determines sex -2 forms -- X & Y -female = XX male = XY -autosomes: 1st 22 pair of chromosomes that code for everything else -examples of sex-linked traits -red-green colorblindness -hemophilia -more common in males because they only have 1X -e.g. eye color in fruit flies is carried on the X chromosome R X – red eyes r X – white eyes (Discovered by Thomas Hunt Morgan) Cross R r X X x r XY 5. Multiple alleles: -a trait is controlled by more than 2 alleles -e.g. blood types = 3 options for alleles (IA, I B, & i) -important for transfusions & paternity cases Genotype IAIA or IAi Surface Phenotype Molecules A A IBIB or IBi B B IAIB AB AB Ii None O -e.g. Mom = Type O (ii) Dad = Type AB (IAIB) -e.g. – Mom = Type A Baby = Type AB Can Dad = Type O? Carrier-individual that is heterozygous for a defective trait -has the recessive allele, but doesn’t have the gene & can pass that on to offspring Pedigree: graphic representation of an ind. family tree Key Female or Male or Affected or Carriers or Parents (P) Offspring (F1) -used mostly to show inheritance of diseases Hemophilia – carried on the X XH – Normal Xh – Hemophilia Karyotype: map showing paired homologous chromosomes -used to determine sex & genetic disorders -Autosomes: 1st 22 pairs of chromosomes -Sex Chromosomes: 23rd pair XX=female XY=male Selective Breeding- org. are bred to have specific traits e.g. dogs, livestock, crops Methods: 1. Inbreeding-mating closely related individuals -creates offspring that are homozygous for desired trait 2. Hybrids-org. created from breeding 2 varieties or closely related species -offspring usually larger & stronger than parents e.g. crop plants & livestock