* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diapositive 1 - univ
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
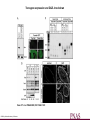
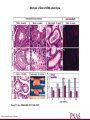
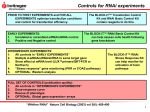
Dazl shRNA construct design Dann C T et al. PNAS 2006;103:11246-11251 ©2006 by National Academy of Sciences Transgene expression and DAZL knockdown Dann C T et al. PNAS 2006;103:11246-11251 ©2006 by National Academy of Sciences Analysis of Dazl-shRNA phenotype Dann C T et al. PNAS 2006;103:11246-11251 ©2006 by National Academy of Sciences Reverse genetics in the rat: Advantages to using in vivo RNAi over traditional knock-out methods • Because of the small size of the sequences encoding shRNAs, these sequences can be cloned in lentiviral vectors • Production of transgenic founders with lentivirus is easy and efficient • In vivo RNAi allows to generate animals with different degrees of gene deficiency. An allelic series of hypomorphs is often more informative for modeling human disease phenotypes • Conditional in vivo RNAi approach is now feasable in the rat using tissue specific promoters (RNA polymerase II promoters) driving the expression of shRNAs (embedded in microRNAs)