* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
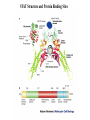
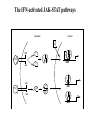
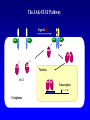
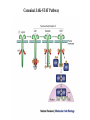
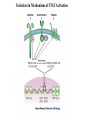
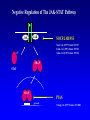
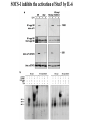
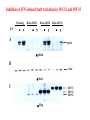
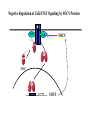
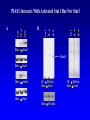
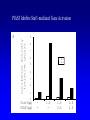
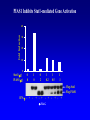
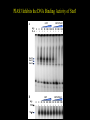
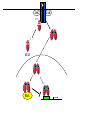
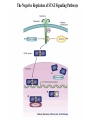
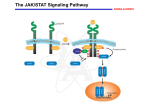
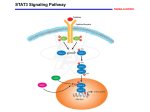
EUKARYOTIC CELL SIGNALING IV & V The JAK-STAT Pathways Dr. Ke Shuai Office: 9-240M Factor Tel: X69168 E-Mail: [email protected] The discovery of the JAK-STAT pathway 1. Using interferons (IFNs) as the model system. IFNs consist of two types: type I (IFN-a, IFN-b) and type II (IFN-g). Type I and II IFNs bind to different receptors and activate overlapping but distinct genes. 2. Identification of genes which are specifically activated by IFN-a and IFN-g, characterizing the specific DNA sequences responsible for IFN stimulation in the promoters of these genes. ISRE: Interferon-a stimulated responsive element GAS: gamma-activation sequence 3. Identification of STATs (signal transducer and activator of transcription) Biochemical purification 4. A genetic approach led to the discovery of the role of JAKs in IFN signaling as well as the importance of STATs in IFN-mediated gene activation. The JAK (Janus Kinase) family JAK1 JAK2 JAK3 Tyk2 STAT: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription N-terminal Domain Coiled Coil Domain DNA Binding Domain SH2 Domain Linker Domain Y701 N1 Transact. Domain -C 136 317 488 576 683 712 750 aa Chen et al. (1998) Cell 93:827-839 Ligand Stat1 (a, b Stat2 Stat3 (a, b Stat4 Stat5A Stat5B Stat6 IFN-a , -b, g IFN-a , -b IFN-a , IL-6, EGF IL-12, IFN-a IL-2, EPO, PRL IL-2, EPO, PRL, GH IL-4, IL-13 In vivo Function Innate immunity IFN-a response Embryonic development Th1 response Mammary gland development, lactation Sexual dimorphism, T cell/ NK cell growth Th2 response STAT Structure and Protein Binding Sites The JAK-STAT Pathway . Activated by a variety of cytokines and growth factors Interferons: IFN-a, -b, g Interleukins: IL-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15 Growth hormones: EPO, GH, PRL Growth factors: EGF, PDGF, CSF-1, G-CSF . Involved in a wide spectrum of physiological settings Cell proliferation Cell differentiation Apoptosis Immunity Development Hematopoiesis The IFN-activated JAK-STAT pathways Nucleus Cytoplasm 48 Tyk2 p 1 48 p IFN-a 1 Jak1 p 1 2 p 2 ISRE 2 p 1a p 1a Jak1 IFN-g 1a/b Jak2 1a/b p GAS p 1a/b p 1b p 1b GAS X The JAK-STAT Pathway Ligand JAK JAK JAK JAK Y JAK P SH2 SH2-P Y SH2 Y SH2 Nucleus STAT Cytoplasm SH2-P Transcription Canonical JAK-STAT Pathway Variations in Mechanisms of STAT Activation Characteristics of STAT signaling 1. JAKs are constitutively associated with the receptor and are activated upon receptor dimerization. 2. STAT pre-exists in the cytoplasm and is activated by tyrosine phosphorylation and then translocates into the nucleus to activate genes. 3. The STAT SH2 domain has dual roles: 1) binding to the receptor 2) forming homo- or heterodimers 4. STAT dimerization is mediated through SH2-phosphotyrosine interactions. Dimerization is required for STAT to bind to DNA. 5. Specificity of the STAT signaling pathways can be achieved at multiple steps. Negative Regulation of The JAK-STAT Pathway JAK JAK SOCS/JAB/SSI Starr et al. (1997) Nature 387:917 Endo et al. (1997) Nature 387:921 Naka et al. (1997) Nature 387:924 Y SH2-P STAT SH2-P PIAS Chung et al. (1997) Science 278:1803 The Structure of SOCS (Suppressor Of Cytokine Signaling) Proteins N C SOCS/JAB/SSI SH2 SOCS Box CIS: cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein SOCS: 1-7 The identification of SOCS-1 in IL-6 signaling Three different approaches were used: 1. Expression cloning 2. Yeast two-hybrid cloning 3. Screening cDNA library with a specific antibody Expression of SOCS-1 suppresses IL-6-induced macrophage differentiation SOCS-1 inhibits the activation of Stat3 by IL-6 Inhibition of IFN-induced Stat1 Activation by SOCS1 and SOCS3 HeLa-hyg IFN : - a g HeLa-SOCS1 - a g HeLa-SOCS2 - A a g HeLa-SOCS3 - a g pStat1 a-pStat1 B Stat1 a-Stat1 C SOCS3 SOCS2 SOCS1 a-Flag Negative Regulation of JAK/STAT Signaling by SOCS Proteins JAK JAK SOCS P-Y SH2 Y SH2-P SH2 STAT SH2-P P-Y SOCS PIAS: protein inhibitor of activated STAT LXXLL Zinc finger region Acidic domain Serine-threoninerich region PIAS1 650 aa PIAS3 583 aa PIASxa 572 aa PIASxb 621 aa PIASy 510 aa The Strategy to Characterize PIAS Proteins in STAT Signaling 1. Preparing specific anti-PIAS antibodies 2. In vivo co-immunoprecipitation analysis 3. Analysis of PIAS effects on STAT-mediated gene activation 4. Study of the molecular mechanisms of PIAS action Blot: IFN IL-6 Unt IFN IL-6 B Unt IFN A IL-6 Unt PIAS3 Interacts with Stat3 but not Stat1 a-pStat1 Stat3 Blot: a-Stat1 Blot: a-pStat3 IP: a-PIAS3c Blot: a-Stat3 Blot: a-Stat3 Blot: a-PIAS3c IP: a-PIAS3c Blot: a-Stat1 IFN IL-6 Unt IFN IL-6 B Unt IFN IL-6 A Unt PIAS1 Interacts With Activated Stat1 But Not Stat3 Blot: a-pStat1 Stat1 Blot: a-Stat1 Blot: a-pStat3 Blot: a-Stat3 IP: a-PIAS1n Blot: a-Stat1 Blot: a-PIAS1n IP: a-PIAS1n Blot: a-Stat3 PIAS3 Inhibits Stat3-mediated Gene Activation A Luciferase Activity (relative units) 9 8 7 6 - IL-6 + IL-6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Stat3(g) PIAS3(g) - 1.0 - 1.0 0.5 1.0 1.0 PIAS1 Inhibits Stat1-mediated Gene Activation Fold Induction 40 30 20 10 0 Stat1 (g) PIAS1 (g) 0 0 1 0 0 2 1 0.2 1 0.5 1 1 Flag-Stat1 Flag-PIAS1 IFN-g: - + - + - + - aFLAG + - + - + PIAS3 Inhibits the DNA Binding Activity of Stat3 A GST (ng) 0 IL-6 - 0 + GST-PIAS3 20 50 100 200 20 50 100 200 + + + + + + + + Stat3/3 Stat1/3 Stat1/1 B (ng) 0 TNF-aNFB GST 0 + 20 + GST-PIAS3 50 100 200 20 50 100 200 + + + + + + + Inhibition of STAT signaling by PIAS 1. PIAS1 and PIAS3 specifically interact with phosphorylated Stat1 and Stat3, respectively, in a ligand-dependent manner. 2. PIAS inhibits STAT-mediated gene activation by blocking the DNA binding activity of STAT. JAK JAK P-Y SH2 SH2-P Y SH2 STAT SH2-P SH2-P P- SH2-P P-Y PIAS The Negative Regulation of STAT Signaling Pathways Summary of techniques used in cell signaling studies A. Identify signaling components 1. Yeast two-hybrid assays 2. Expression cloning 3. Searching for family members: computer search; degeneraged PCR strategy as well as low stringency cDNA library screening 4. Biochemical purification 5. Protein complex pull-down by immunoprecipitation followed by mass spectrometry analysis 6. Genetics B. Protein-protein interactions 1. Yeast two-hybrid assays 2. Co-immunoprecipitation analysis: endogenous or cooverexpression 3. In vitro binding : GST-pull down, etc. 4. Far Western analysis C. Functional assays 1. Reporter gene assays, Northern blot analysis 2. EMSA (gel shift) 3. Modification analysis: labeling, immunoprecipitation followed by specific antibody, identify site and mutate and test its importance 4. Dominant negative or constitutive active mutants 5. Antisense 6. Knock-outs