* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Isozymes
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Personalized medicine wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
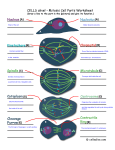
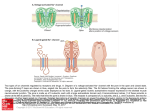
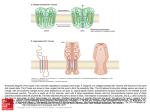
molecular revolution The first molecular markers: allozymes Allozymes Enzymes that diifer in amino acid sequence yet catalyze the same reaction -visible as a band on a gel -may exist at several gene loci Isozyme: allelic form of allozyme (same locus) + Allozyme assay • Gel electrophoresis • Current • Charge • Gel matrix • Starch or other medium • Protein variation • Charge • depends on pH Substrate • Size • different length of AA chain • Shape • Tertiary and quaternary structure • Visualization • Uses enzyme reactions • Specific substrate for each allozyme enzyme Visible Product Lab assay of isozymes Isozyme gels Quaternary Structure and Allozymes • Enzymes can consist of several subunits • Monomer • One subunit – Dimer • Two subunits – Tetramer • Four subunits AA Genotype AB BB Disparate viewpoints about true levels of genetic variation • classical + + + m + ... + + + ============== + + + + + ... + + + • balanced A1 B2 C3... X1 Y1 Z3 ================= A4 B2 C7... X1 Y1 Z2 Allozymes revealed unexpectedly high levels of genetic variation Allozyme questions • What type of DNA variation can you detect with isozymes? • What is the ascertainment bias? • Why were they wildly popular in the 1970’s and 1980’s, then disappeared by 2000?