* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 15 - People Server at UNCW
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
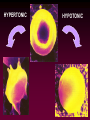
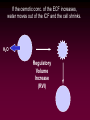
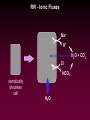
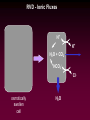
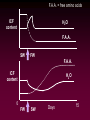
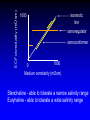
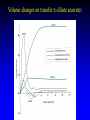
Osmotic and Ionic Regulation All animals face osmotic and ionic stresses. Stresses depend on environment: • Aquatic • Marine • Freshwater • Brackish (estuarine) • Terrestrial SW inve r Elas t. mob ranc h Tele ost FW inve rt. ICFConc.(mOsm) BlodConc.(mOsm) 1 0 0 0 io n s o r g a n ic s 5 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 io n s o r g a n ic s 5 0 0 0 Regardless of their environment, all animals must be capable of maintaining isosmoticity between the ICF (intracellular fluid) and ECF (extracellular fluid). Regulating ICF osmotic conc. in response to changes in the osmotic conc. of the ECF is called: Cell Volume Regulation HYPERTONIC HYPOTONIC Unchecked swelling under hypotonic conditions can lead to OSMOTIC LYSIS If the osmotic conc. of the ECF decreases, water moves into the ICF and the cell swells. H2O Regulatory Volume Decrease (RVD) If the osmotic conc. of the ECF increases, water moves out of the ICF and the cell shrinks. H2O Regulatory Volume Increase (RVI) RVI - Ionic Fluxes Na+ H+ H2O + CO2 ClHCO3osmotically shrunken cell H2O RVD - Ionic Fluxes H+ K+ H2O + CO2 HCO3Cl- osmotically swollen cell H2O F.A.A. = free amino acids ICF content H2O F.A.A. SW FW F.A.A. ICF content H2O 0 FW SW Days 15 Animals can reduce the amount of volume regulation their cells must do by regulating ECF osmotic concentrations. Osmotic and ionic regulation occurs in both aquatic and terrestrial spp. We’ll look at aquatic organisms first ECF osmolarity (mOsm) 1000 isosmotic line osmoregulator osmoconformer 1000 0 Medium osmolarity (mOsm) Stenohaline - able to tolerate a narrow salinity range Euryhaline - able to tolerate a wide salinity range Volume changes on transfer to dilute seawater