* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry - Solutions
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Properties of water wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Solvent models wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
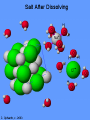
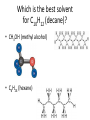
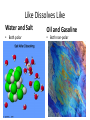
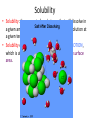
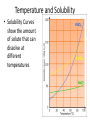
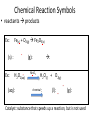
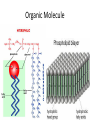
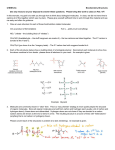
Chemistry - Solutions Mixtures • Physical blend of 2 or more things • 2 Types: – Heterogeneous: composition is not uniform – Homogeneous: composition is uniform • Can be separated physically (ex. pouring, filtrating, chromatography, distillation) Homogeneous Mixtures • All solutions are homogeneous Solution: mixture of two or more substances, the solute and the solvent. Solvent vs. Solute… • Solvent: the dissolving medium – Ex: Water • Solute: the dissolved substance – Ex: sugar How Stuff Dissolves • Occurs when the attraction between the solvent and the solute is GREATER than between the parts of the solute. • LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE Which is the best solvent for C10H12 (decane)? • CH3OH (methyl alcohol) • C6H14 (hexane) Polar vs. Non-polar • Polar molecules – Have an unequal distribution of electrical charge – Causes partial positive charge and partial negative charge • Non-polar molecules – Have equal sharing of electrons – Charge distribution is the same throughout molecule Like Dissolves Like Water and Salt • Both polar Oil and Gasoline • Both non-polar Solubility • Solubility: the amount of a substance that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent to form a saturated solution at a given temperature • Solubility depends on RANDOM MOLECULAR MOTION, which is affected by temperature, pressure and surface area. Temperature & Motion Inquiry Lab Purpose: Determine which is more effective, temperature or motion, in increasing the rate of solubility of sugar in water. Hypothesis: ? Materials: Triple beam balance, graduated cylinders, beakers, hot water, tap water, stir sticks and thermometers. Procedure: ? Data/Observations (include table): ? Conclusion: ? Temperature and Dissolving? • Which dissolves faster: sugar in hot tea or sugar in ice tea Higher temperatures = faster dissolving due to greater kinetic energy of water molecules Temperature and Solubility • Solubility Curves show the amount of solute that can dissolve at different temperatures Pressure and Dissolving? • Which has more bubbles Just opened Soda or Soda that has been left out Bubbles in Soda = CO2 Higher pressure = more dissolved gas. Pressure has little/no effect on dissolving solids Surface Area and Dissolving? • What dissolves faster Cube of Sugar or Spoonful of Sugar Smaller particle size = faster dissolving More surface that is exposed = faster dissolving Chemistry – Balancing Chemical Equations Families of Elements Chemical Formulas Chemical Symbols H2O States what elements are in the compound Every element has a different letter Subscript How many atoms of that element are in the compound Chemical Equation • Chemical Equation: Summarizes the details of a chemical reaction – Chemical reaction: Breaking and forming of chemical bonds Diatomic Molecule: Reactants Exist as two bonded atoms of the same Chemical Reactions are element Products Balanced Ex: O2, H2, Cl2, N2, Br2, I2, F2 Balancing Reactions Activity H = White Ball O = Red Ball C = Black Ball • React one H2 with one O2 by splitting the molecules and joining one O atom to two H atoms. Because there is unreacted O, you must react it with another H2 to form another water molecule. – Summarize what happened ___H2 + ___O2 ___H2O • React methane (CH4) with oxygen (O2) to produce Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Continue reacting molecules of CH4 and O2 until all reactant atoms have formed products – Summarize what happened ___CH4 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O Keeping Track of Atoms 2H2 + O2 2H2O Reactants Products Law of Conservation of Mass: Mass of Reactants = Mass of Products In a Chemical Reaction, Matter is neither created nor destroyed! Chemical Reaction Symbols • reactants products Ex: Fe(s) + O2(g) Fe2O3(s) (s) : Ex: : (g): H2O2(aq) (aq): MnO2 H2O(l) + O2(g) chemical : (l): (g): Catalyst: substance that speeds up a reaction, but is not used Balancing Equations 1. Determine Formulas hydrogen gas = H2 oxygen gas = O2 water = H2O 2. Write the equation H2 + O2 H2O 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element in the reactants and products Reactants hydrogen: 2 oxygen : 2 Products hydrogen: 2 oxygen : 1 Balancing Equations 4. Next use coefficients to balance the elements H2 + O2 hydrogen: 2 oxygen: 2 2H2 + O2 hydrogen: 4 oxygen: 2 H2O hydrogen: 2 oxygen: 1 2H2O hydrogen: 4 oxygen: 2 DO NOT CHANGE SUBSCRIPTS! 5. Make sure all coefficients are the lowest possible ratio Balancing Equations • Methane gas (CH4) reacts with chlorine gas (Cl2) in sewage treatment plants to create liquid chloroform (CHCl3) and hydrogen chloride gas (HCl). What would a balanced chemical equation look like for this reaction? Balance these equations ① AgNO3 + H2S Ag2S + HNO3 ② Zn(OH)2 + H3PO4 Zn3(PO4)2 + H2O Balance these Equations ① FeCl3 + NaOH Fe(OH)3 + NaCl ② CS2 + Cl2 CCl4 + S2Cl2 1. Label the products and reactants in the following equation: Iron + oxygen Iron (III) oxide 2. Balance the following equation: H2(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) Organic Chemistry It’s all about CARBON Organic Molecules • Covalent Bonds – electrons are shared • Polymers: large molecules made by repeating subunits – DNA – Protein – Carbohydrates • Made possible by Carbon Organic Molecules • DNA – Subunit: Nucleotide Organic Molecules • Protein – Subunit: amino acids Organic Molecules • Carbohydrates – Subunits: Saccharides or Monosaccharides (sugars) Organic Molecule • Lipids – Fatty Acids (Make up cell membrane) – Contains repeating hydrocarbons