* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
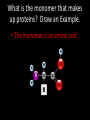
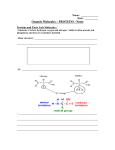
Proteins Sec 2.7 pg 37-39 • Last day’s homework: –Read the protein summary sheet & highlight big ideas –Answer 4 qs on back side of summary What is the monomer that makes up proteins? Draw an Example. • The monomer is an amino acid. * How to Identify an Amino Acid • Central Carbon bonded to a Hydrogen AND: i) Amino Group –NH2 ii) Acidic Group –COOH iii) “R” group- remainder group differs between amino acids What is the generic name of a long chain of amino acids? • A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. How do amino acids bind together to form a dipeptide? Draw the process • Condensation synthesis! Peptide Bonds: – form between amino acids & join them – Amine group combines with carboxyl group of next amino acid – Atoms of O,C, C & H share electrons (unevenly) – Polar bond (O is more neg, H is more pos) Complete the table about the levels of organization in a protein Level of Organization Description of Shape Type of Bond Primary Linear Peptide bonds Secondary Alpha-helix or Pleated sheet Hydrogen bonds Tertiary 3-D structure Bonds between R groups: Can involve Hydrogen bonds, covalent, or ionic bonds or disulfide bonds all can occur Quaternary When 2 or more polypeptide chains join together Bonds between R groups also! (many different kinds) Today’s Mission • Build me pipe cleaner protein in partners! • Follow instructions 1-6 and show me your final protein • Complete the Qs on the handout as you go!