* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration Powerpoint1
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
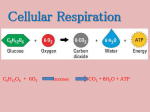
Chapter 8 Cellular Respiration Chemical Pathways One gram of the glucose, releases 3811 calories of heat energy when burned aerobically A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius Cells release the energy from glucose and other food compounds Cellular Respiration Process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen Takes place in the mitochondria C6H12O6 + 6 O2 ----> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP Occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and ETC Glycolysis Is the first step of cellular respiration It is an anaerobic process which means that it does not require oxygen to proceed Requires an input of energy (ATP) Occurs in the cytoplasm Is the splitting of sugar (glucose) Releases only a small amount of energy but the process is fast; can produce thousands of ATP molecules in a few milliseconds Produces two molecules of a 3 carbon compound, PGA The net yield is 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 molecules of pyruvate Fermentation Anaerobic process that follows glycolysis when oxygen is not available to the cell. Converts pyruvate and NADH into NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue Alcoholic Fermentation Is useful to the beer, wine and baking industries Another way in which NADH is converted back to NAD+ Produces alcohol, NAD⁺ and CO2 The CO2 produced by yeast makes the dough rise and bubbles appear in beer and sparkling wines Pyruvic acid + NADH–> Alcohol +CO2+ + Lactic Acid Fermentation Occurs in the muscle cells of animals One way in which NADH is converted back to NAD+ Lactic acid and NAD⁺ are produced Occurs when we exercise, and our body has used up all of the ATP. Our muscles start burning and are sore after exercising. It also causes muscle fatigue. Pyruvic Acid + NADH—>Lactic Acid + NAD+ The CAC, Krebs Cycle, or TCA Cycle (2nd Step of Cellular Respiration) Follows glycolysis if oxygen is available to the cell Pyruvic acid travels from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria and is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy extracting reactions Is an aerobic process (requires oxygen) Steps of the CAC Cycle, Krebs Cycle, or the TCA Cycle 1. 2. 3. Pyruvic acid is broken down into CO2 and 2C Acetyl groups which is bound briefly to acetyl CoA 2 Carbons are passed into the Kreb Cycle to combine with a 4 carbon compound, (Oxaloacetate), to produce a 6C compound, citric acid. 2 C atoms are removed (in 2 molecules of CO2) Steps Cont’d 4. 5. 6. 3 Molecules of NAD+ are converted to NADH 1 Molecules of FAD converted to FADH2 1 Molecule of ADP converted to ATP or GDP to GTP Cycles through twice to breakdown down both molecules of pyruvate Electron Transport in the Mitochondria (3rd Step of Cellular Respiration) Is a series of molecules along which electrons are transferred, releasing energy Carrier molecules bring electrons from glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle to the ETC The molecules are located on the inner membranes of the mitochondria Is an aerobic process because oxygen is the final electron acceptor Electron Transport in the Mitochondria (3rd Step of Cellular Respiration) Carrier molecules NADH and FADH2 give up electrons that pass through a series of reactions At least 15 carrier proteins are involved in the ETC At the top of the chain, the electrons have high energy, as they pass through the ETC, the energy given off is captured in molecules of ATP Electron Transport in the Mitochondria (3rd Step of Cellular Respiration) High Energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along a series of E.T. enzymes in the inner membrane of the mitochondria At the end of the chain, an enzyme combines electrons from the ETC, H+, and O2 from H20 Produces 34 molecules of ATP ATP formation H+ ions are pumped from the inside of the IM to the outside The outside is more positively charged than the inside The difference in charge supplies energy to make ATP from ADP Adenine Phosphate Groups ATP Molecule Ribose Energy in Balance Photosynthesis-deposits energy Respiration-withdraws energy The equation from photosynthesis and the complete breakdown of glucose are the reverse of each other The products of photosynthesis are the reactants of cellular respiration and vice versa Total ATP Production Glycolysis-net gain of ATP =2 ATP 2 NADH x 3 ATP =6 ATP Pyruvate into Acetyl CoA 1 NADH x 3 ATP x 2 cycles =6 ATP Krebs Cycle =2 ATP 3 NADH x 3 ATP x 2 cycles =18 ATP 1 FADH2 x 2 ATP x 2 cycles =4 ATP Total =38 ATP (prokaryotes) Eukaryotes use 2 ATP traveling from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria resulting in 36 ATP Overview of Cellular Respiration Begins with glycolysis Krebs Cycle is 2nd stage Electron Transport Chain is the 3rd stage; transports eResults in the formation of 36-38 molecules of ATP C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP