* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
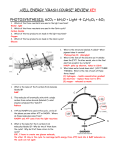
Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Krebs cycle Electron transport Learning check This figure represents an overview of the different processes of cellular respiration. Which of the following correctly identifies the different processes? a) 1. Glycolysis; 2. Electron transport chain; 3. Krebs cycle b) 1. Glycolysis; 2. Krebs cycle; 3. Electron transport chain c) 1. Krebs cycle; 2. Electron transport chain; 3. Glycolysis d) 1. Electron transport chain; 2. Glycolysis; 3. Krebs cycle What would happen to the flow of electrons if oxygen were not present? a. The flow of electrons would continue but at a slower rate. b. The flow would cease and ATP production would stop. c. The presence of oxygen would have no effect. Cyanide binds strongly with the last electron carrier in the chain. How would this affect the flow of electrons? a. The flow of electrons would continue but at a slower rate. b. The flow would cease and ATP production would stop. c. The presence of cyanide would have no effect. How many ATPs? Cell Respiration Overview Glucose: Stores energy in the molecule Cell respiration: • Breaks down the molecules • Extracts the contained energy • Transfers electrons (from glucose) • To hydrogen carriers (e.g., NADH) • And to make ATP • Giving off waste products (CO2 & H2O) 1st stage: Cytoplasm 2nd & 3rd stage: Mitochondria 1st stage: Glycolysis 2nd stage: Krebs cycle (or citric acid) 3rd stage: Electron transport Glycolysis, in the cytoplasm Series of steps (but 2 phases) 1. Glucose 2 pyruvic acid molecules As bonds in glucose are broken 2. Electrons (and H+ ions) NAD+ NADH Glucose Is oxidized NAD+ Is reduced Net output is 2 ATP for each glucose molecule But, most of the released energy carried by NADH Glucose 2 pyruvic acids Phase one 3 carbon 6 carbon 3 carbon Glycolysis, phase 1 Some ATP is used to start the ‘breakdown’ of glucose Mitochondria Cytoplasm View Activity: Glycolysis Glycolysis, phase 2 High energy electrons are donated To NAD+ Forming NADH Glycolysis, phase 2 And, phosphate groups are transferred ATP is made In-between glycolysis & Krebs Just before (or as) they enter the mitochondria Pyruvic acid molecules are modified And CO2 is released The altered molecule is acetic acid (…vinegar!) Acetic acid is attached to a carrier molecule Called coenzyme A And forms acetyl CoA To the mitochondrion Learning check 7 3 4 2 1 6 8 5 1. 2. 3. 4. Name molecule Name molecule Name molecule Name the reaction 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Name of molecule What does the arrow refer to? Name of molecule Name of molecule Where does this take place? Krebs cycle, in the mitochondria Series of reactions Continues to break down the sugar Present as acetic acid Captures more energy As NADH & FADH2 And more CO2 is released Net output is 2 ATP for each glucose molecule But again, most of the released energy carried by NADH Krebs (citric acid) cycle & energy production Citric acid Fuel: Acetic acid 3 Waste: 2 CO2 3 Acceptor molecule View Activity: The Citric Acid Cycle Electron Transport, in the mitochondria Most of the ATP is produced in the ET And, NADH & FADH donate their electrons to the ET At the end of the chain of steps O2 exerts a strong pull on electrons And combines electrons & H+ ions to form H2O The ‘downhill’ flow of electrons powers an enzyme ATP synthase Which produces ~ 34 ATP Electron Transport An array of molecules (…proteins) In the inner membrane of the mitochondrion View Activity: Electron Transport Electrons move from one member to the next The energy given up pumps H+ to inner space Matrix Oxygen captures electrons Hydrogens are added, water forms The buildup of H+ ions give up energy When they diffuse through a special protein Matrix ATP synthase ATP synthase captures their energy To make ATP Learning check, name the numbered parts How many? 4 15 10 11 7 1 2 6 3 9 14 12 8 13 5 18 16 17 Learning check 1. Of the 3 stages of cell respiration, which produces the most ATP per glucose? 2. In glycolysis, _______ is oxidized and _______ is reduced. 3. The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chains in mitochondria is _______. Learning check 4. Cells can harvest the most chemical energy from which of the following? a. An NADH molecule b. A glucose molecule c. Six carbon dioxide molecules d. Two pyruvic acid molecules