* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 4 & 5 - Organic Chemistry
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Natural product wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
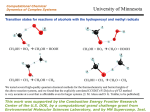
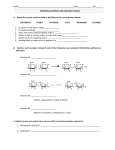
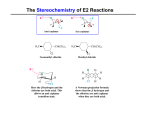
During the early part of World War II a brigade of French soldiers were trapped by a superior force of German force and unable to escape. The French were without adequate food and virtually out of water for several hot September days. When they finally escaped the encirclement, the soldiers retreated. They came across a farm with many bee hives and quickly removed the combs and ate large amounts of honey. All but one perished within several hours. WHY??? (They did not die from enemy fire or bee stings.) Organic Chemistry Carbon • Living things are mostly made of very few elements •CHONPS • Carbon is the most useful • Plants take in carbon from CO2 . Carbon • Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Vitalism vs. mechanism. Remember Miller? Isomers • Structural • Geometric • Enantiomers Isomers • Structural vs. • Geometric • Enantiomers Isomers • Structural vs. • Geometric vs. • Enantiomers Isomers • Structural vs. • Geometric vs. • Enantiomers vs. Functional Groups • • • • • • hydroxyl carbonyl carboxyl amino sulfhydryl phosphate -OH >CO -COOH -NH2 -SH -OPO32- ATP • Adenosine triphosphate is the primary energy source for the cell ℗-℗-℗-adenosine ATP → ADP + energy. Macromolecules • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Proteins • Nucleic acids. Carbohydrates • Sugars (CH2O) • Dehydration → polymers • Storage polymers • Structural polysaccharides . Dehydration synthesis: Dehydration synthesis: Dehydration synthesis: Dehydration synthesis: Dehydration synthesis: Dehydration synthesis: Dehydration synthesis: CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 2OH starch CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH cellulose 2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH Lipids • Fats • Fatty acid has hydroxyl group • Triglycerides • Saturated and unsaturated • Phospholipids • Steroids. fatty acid fatty acid glycerol dehydration synthesis dehydration synthesis dehydration synthesis triglyceride saturated saturated unsaturated phospholipid CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 cholesterol OH OH CH3 CH3 testosterone O OH CH3 estradiol OH Concept Check Questions Concept Check Questions Draw a structural formula for C2H4. Concept Check Questions What is the chemical similarity between gasoline and fat? Concept Check Questions What does the term “amino acid” signify about the structure of such a molecule? Concept Check Questions How many molecules of water are needed to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 10 monomers long? Concept Check Questions After you eat a slice of apple, which reactions must occur for the amino acid monomers in the protein of the apple to be converted into proteins in your body? Concept Check Questions A dehydration reaction joins two glucose molecules to form maltose. The formula for glucose is C6H12O6. what is the formula for maltose? Concept Check Questions Compare and contrast starch and cellulose. Concept Check Questions Compare the structure of a fat with that of a phospholipid. Concept Check Questions How do saturated fats differ from unsaturated fats, both in structure and behavior? .