* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecule Wkst
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
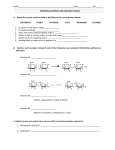
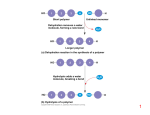
Macromolecules Worksheet Name: ________________________Per. 1 2 3 4 Part A. Classify each as a carbohydrate, protein, lipid or nucleic acid. 1. starch 10. polysaccharide 2. cholesterol 11. phospholipid 3. steroid 12. glycerol 4. glycogen 13. monosaccharide 5. nucleotide 14. cellulose 6. RNA 15. amino acid 7. polypeptide chain 16. enzyme 8. glucose unsaturated fatty acid 17. saturated fat 18. DNA 9. Part B. Identify the specific molecule (use the above terms) from each description. Some terms may be used more than once. 19. forms the cell membrane of all cells 20. speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 21. one sugar 22. cells convert this into ATP 23. monomer of proteins 24. steroid that makes up part of the cell membranes 25. 3-carbon “backbone” of a fat 26. monomer of nucleic acids 27. forms the cell wall of plant cells 28. provides long-term energy storage for animals 29. sex hormones Part C. Which specific molecule (saturated fat, unsaturated fat, protein, glucose, starch, cellulose) is each food mostly made of? 36. almond 43. wheat 37. spinach 44. celery 38. beef jerky 46. cranberries 39. bacon 47. egg white 40. noodles 48. table sugar 41. orange juice 49. popcorn 42. cheese 50. lobster Part D. Beside each carbohydrate molecule, write whether is monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide. 1. 2. 3. Part E. Each of the following structures below shows a fatty acid molecule. On the line, identify the fatty acid as saturated, unsaturated, or polyunsaturated. 1. 2. 3. Part F. Macromolecule questions 1. All organic compounds contain the element . 2. What is the difference between monosaccharide, disaccharide, & polysaccharide? 3. What 3 elements make up carbohydrates? a. b. c. 4. (Circle one) Lipids are polar or non-polar. 5. (Circle one) Lipids are or aren’t soluble in water 6. What kind of bond holds water molecules together and strands of DNA? 7. (Circle one) Enzymes typically end in –ase or –ose 8. (Circle one) Sugars tend to end in –ase or –ose 9. What are the 2 types of sugars found in nucleic acids? a. DNA sugar: b. RNA sugar: 10. (Circle one) The reaction below is showing hydrolysis or dehydration synthesis? Maltose + water Glucose + Glucose a. What are the reactants? 11. (Circle one) The reaction below is showing hydrolysis or dehydration synthesis? Glucose + Glucose Maltose + water a. What are the products? Part G. Dehydration Synthesis & Hydrolysis Below is an example of dehydration synthesis. In dehydration synthesis, a hydrogen atom from one molecule joins with a hydroxyl group (-OH) from another molecule to form water, leaving two molecules bonded to the same oxygen atom. For example, when glucose and glucose combine by dehydration synthesis, they form maltose and water. + H 2O + Glucose Glucose Maltose Below is an example of hydrolysis. Complex organic molecules are broken down by the addition of the components of water – H+ and OH-. water 1. What are the products of the hydrolysis reaction? 2. What are the reactants of the dehydration synthesis reaction? 3. How are the reactions in #5 and #6 related? 4. Look at the three reactions below. Which reaction reaction(s) is hydrolysis taking place? a. How do you know? 5. Look at the three reactions below. Which reaction(s) is dehydration synthesis taking place in? a. How do you know?