* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hydrolysis and Dehydration Synthesis: How we become what we eat
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
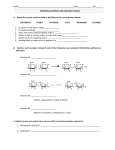
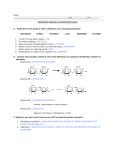
Hydrolysis and Dehydration Synthesis: How we become what we eat. Hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis are chemical processes used to break down and rebuild organic compounds. Organic Compounds: o Carbohydrates (Sugars and Starches) o Monosaccharides are simple sugars, i.e., glucose and fructose o Complex carbohydrates form when glucose bonds with another monosaccharide o Lipids o Triglycerides – 3 fatty acids + glyceride o Steroids – cholesterol and hormones o Protein o Made of amino acids o Enzymes speed up chemical reactions o Structural proteins (hair) o Nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) Dehydration Synthesis: o Chemical process through which small molecules (monomers) join together (bind) to make large molecules (polymers) and water (H2O)is removed o During process, a hydrogen (H+) ion from one molecule and a hydroxide (OH-) ion from the next molecule are removed o This process builds what our bodies need. o Small molecules become more complex molecules. o Monosaccharides → Complex Carbohydrates o Amino Acids → Proteins o Nucleotides → Nucleic acid Hydrolysis: o Chemical process whereby large molecules are broken down when water is added o During process, a hydrogen (H+) ion is added to one molecule and a hydroxide (OH-) ion is added to the next molecule. o This process converts foods we eat into nutrients our bodies can use o Large food molecules changed into smaller, simpler molecules. o Sucrose + Water → Glucose + Fructose (Disaccharide → 2 Monosaccharides) Role of Hydrolysis and Dehydration Synthesis in Digestion: Through hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis, foods that are digested are changed into their organic compounds to perform important functions in maintaining our bodies: o Carbohydrates – provide energy o Lipids – store energy, provide insulation, function as hormones o Proteins – assist with muscle development and tissue health