* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
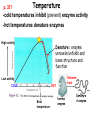
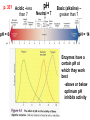
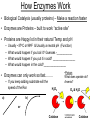
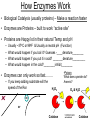
A&P 120 Enzyme Function Exercise 4 www.celltech.com/resources/vt/enzymes.html Terminology • Metabolism – Definition: The sum total of all biochemical activity that takes place in a living organism • Catabolic Metabolism – break down – AB = A & B • Anabolic Metabolism – build up – A + B = AB • In vitro – out of the body (or in a tube) – In Vivo – in the body • Substrate - The material being acted upon Introduction • Enzyme – a protein that is a organic catalyst – Hint: Most of the time ends in –ase • Catalyst – speeds up the rate of a reaction – Catalase – is the name of an enzyme in your body • Active Site – a pocket at the outside of the enzyme specific to a substrate (here is where it is taken apart or put together) Bubbles H2O2 Catalase 2H2O2 Catalase (organic) 2H2O +O2 (Hydrogen peroxide) (Water & Oxygen) Substrate Product H2O2 **Oxygen will bubble in vitro** Catalase p. 35? Temperature -cold temperatures inhibit (prevent) enzyme activity -hot temperatures denature enzymes High activity Denature: enzyme unravels/unfolds and loses structure and function Extreme heat Low activity COLD HOT Best temperature Normal enzyme Denature d enzyme p. 35? pH = 0 Acidic –less than 7 pH Neutral = 7 Basic (alkaline) – greater than 7 pH = 14 Enzymes have a certain pH at which they work best -above or below optimum pH inhibits activity How Enzymes Work • Biological Catalysis (usually proteins) – Make a reaction faster • Enzymes are Proteins – built to work “active site” • Proteins are Happy’ist in their natural Temp and pH – – – – Usually ~370C or 980F & Usually a neutral pH (Function) What would happen if you boil it? Guesses -___________ What would happen if you put it in acid? ________________ What would happen in the cold?________________ • Enzymes can only work so fast…….. – If you keep adding substrate will the speed of the Rxn a) H2O2 •Poison What does cyanide do? Arsenic? O2 & H2O b) or Catalase Catalase How Enzymes Work • Biological Catalysis (usually proteins) – Make a reaction faster • Enzymes are Proteins – built to work “active site” • Proteins are Happy’ist in their natural Temp and pH – – – – Usually ~370C or 980F & Usually a neutral pH (Function) What would happen if you boil it? Guesses -____denature________ What would happen if you put it in acid? _______denature_________ What would happen in the cold?________inhibit________ • Enzymes can only work so fast…….. – If you keep adding substrate will the speed of the Rxn a) H2O2 •Poison What does cyanide do? Arsenic? O2 & H2O b) or Catalase Catalase