* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 19: Blood
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
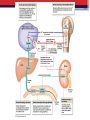
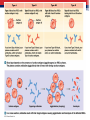
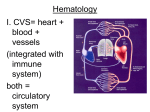
Ch. 19: Blood Fluid connective tissue with cells suspended in a fluid matrix Cardiovascular system • Cardio = heart; acts as pump • Vascular = series of tubes; connections • Body has over 75 trillion total cells 19.1 Functions of Blood • TRANSPORT and DELIVERY of nutrients like sugar and amino acids, O2, elimination of wastes like NH4 ▫ Cells without blood supply die in about 4 minutes • DEFENSE of the body ▫ Antigens and antibodies of immune system • REGULATION of ions and pH • CLOTTING to decrease blood volume lost • Regulation of TEMPERATURE Physical Characteristics of Blood • • • • • “whole blood” 38 C or 100 F 5X viscosity of water 7.35 – 7.45 pH Volume = 7% of mass ▫ 150 pounds = roughly 5 L ( or 5 quarts) 5 liters is about 11 pints ▫ Full grown adult male – 5 to 5.5 L ▫ Full grown adult female – 4 to 5 L 19.2 Plasma • 46 – 63 % of blood volume ▫ 7 % proteins = albumin (60% for pressure), globulin (35 % antibodies), fibrinogen (4 % clotting), mostly from the liver ▫ 1 % solutes = fatty acids, amino acids, Na, K, Cl, Ca, Mg, HCO3, HPO4, SO4 ▫ 92 % water • Ringer’s solution ▫ Isotonic saline solution used to maintain volume; doesn’t carry any O2 • Artificial Blood – current research 19.3 Formed elements • 37 – 54 % of blood ▫ < 1 % platelets ▫ < 1% WBC (white blood cells) ▫ 99% RBC (red blood cells) 19.3 Red Blood Cells • • • • • • • • 260 million RBS in every ‘drop’ of blood Total amount ~ 25 trillion RBCs in 5 L 1000 RBC : 1 WBC Biconcave disc for maximum SA : Vol Stack as they go through capillaries Lose nuclei – so can not divide Last 120 days ( 700 miles) Formed in red marrow, liver, spleen, thymus by erythropoiesis • Recycled by liver , spleen and marrow 19.4 Blood Typing • Over 50 surface antigens • Only usually worry about A/B and Rh +/• Is blood is mis-matched agglutination (clumping or clotting) will occur • Type (genetic genotype) antigen antibodies ▫ “A” (AA, AO) ▫ “B” (BB, BO) ▫ “AB” (AB) A B B A A and B none ▫ “O” (OO) “zero” A and B get given to A, O B, O A B A, B, AB, O AB O All 19.5 White Blood Cells • • • • • • White because lack hemoglobin ( leuko = white) Seen with Wrights stain All can migrate through connective tissues All can do amoeboid movement All have positive chemotaxis Neutrinophils, eosinophils and monocytes can all perform phagocytosis. WBC Types • Granular ▫ Neutrinophils; 1st to injury, nonspecific ▫ Eosinophils; attack cells with anitbodies, parasitic infections, nonspecific, increase during allergic reactions ▫ Basophils; histamine, dilation of blood vessels, nonspecific • Agranular ▫ Monocytes; phagocytic, nonspecific ▫ Lymphocytes ; specific immune reactions T cells – cell mediated immunity B cells – humoral immunity Killer cells – immune system surveillance 19.6 Platelets • Cell fragments • Used to help form clots ▫ Chemical reaction ▫ Physical patch ▫ Shrink clot 19.7 Clotting vs. Shock • Clotting ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Vessel contracts Platelets aggregate and form plug Need vitamin K and Ca +2 to form clots Prostaglandins – regulate clotting Heparin – impedes clotting Aspirin (NSAIDS) – decrease prostaglandins, increase bleeding time • Shock ▫ Loss of blood so that pressure can not be maintained