* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
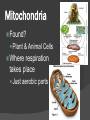
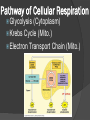
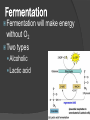
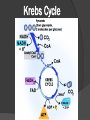
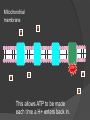
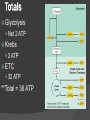
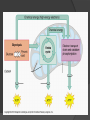
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration The process that releases energy (ATP) by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen Mitochondria Found? Plant & Animal Cells Where respiration takes place Just aerobic parts Aerobic Vs. Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic = presence Respiration Anaerobic of O2 = absence of O2 Fermentation Pathway of Cellular Respiration Glycolysis (Cytoplasm) Krebs Cycle (Mito.) Electron Transport Chain (Mito.) Glycolysis “Glukus” = sweet “Lysis” = loosening Occurs in Cytoplasm Breaking one glucose down into 2 pyruvic acids(3 Carbon) & 2 ATP (net) After Glycolysis Anaerobic = Fermentation Aerobic = Cellular Respiration Fermentation Fermentation without O2 Two types Alcoholic Lactic acid will make energy Alcoholic Yeast & other microorganisms CO2 causes bread to rise Lactic Acid Animal muscles Happens during vigorous exercise Builds up in muscles causing cramps Krebs Cycle Follows glycolysis Needs oxygen Respiration Occurs in mitochondria Breaks down products of glycolysis into carbon dioxide Releasing energy to make electron carriers and ATP Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Inner membrane of mitochondria Electrons move to produce energy ETC: – 2-3 per electron carrier Oxygen is used as the final electron acceptor (H+) Forms water Makes ATP Mitochondrial membrane NADH NADH enters and releases an H+ and an electron. Mitochondrial membrane e- NAD+ NADH enters and releases an H+ and an electron. Mitochondrial membrane eO H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ The electron travels to the next protein while simultaneously sending H+ across the membrane Mitochondrial membrane H+ H+ H+ H2O H+ H+ H+ ADP P The electron is used to form water. The H+ then are pumped back into the mitochondria. Mitochondrial membrane H+ H+ ATP H+ H+ H+ H+ This allows ATP to be made each time a H+ enters back in. Totals Glycolysis Net 2 ATP Krebs 2 ATP ETC 32 ATP **Total = 36 ATP Photosynthesis Vs Cellular Respiration