* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Overview - Greensburg.k12.in.us
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
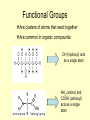
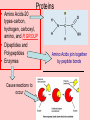
Chapter 3 Overview Biochemistry Section 1-Carbon Compounds • Water is needed by all living things BUT • Carbon is what all living things are made of Organic vs. Inorganic Compounds Inorganic compounds do NOT contain carbon atoms Organic compounds are made mostly of CARBON In living things, if it is not water, it probably is carbon Ionic and Covalent Bonds • What is the difference between ionic and covalent? http://ithacasciencezone.com/chemzone/lessons/03bonding/dogbonds.htm Organic or Inorganic? Organic Compounds Carbon has 4 electrons in outer energy level How many needed in outer shell to be stable? Carbon bonds easily with other atoms Carbon will often bond with itself 2 electrons being shared Organic Compounds • Contain Carbon • Carbon can have single, double, or triple bonds Functional Groups Are clusters of atoms that react together Are common in organic compounds OH (hydroxyl) acts as a single atom NH2 (amino) and COOH (carboxyl) acts as a single atom Large Carbon Molecules • Monomers-similar to functional groups but slightly larger • Polymers-repeating chains of monomers • Macromolecules-repeating polymers creating Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Linking and Breaking Apart • Condensation Reaction • Hydrolysis DS=Condensation Reaction Cells also have the ability to break down polymers using a process called hydrolysis. During hydrolysis, a water molecule is added to the polymer to break it apart (See right). Monomers are joined together by cells to form polymers during a process called dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction). During dehydration synthesis, a hydroxyl (OH) group is removed from one monomer and a hydrogen is removed from the other to join them together to form a polymer. During this process, water is produced (see left). Energy Currency • ATP Section 2 Molecules of Life • • • • Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 1C:2H:1O Ratio Source of energy OR used by body as STRUCTURAL material • Monosaccharides-simple sugar • Disaccharides-double sugar • Polysaccharides-3 or more saccharides Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen (in that order) Ratio of 1:2:1 (CH20)n where n can be any number, what if n= 2, 6, 9, 20? Monosaccharides -monomer carbohydrate -Glucose (cell energy) -Fructose (sweetest, fruits) -Galactose (milk) Protein Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen AND nitrogen Amino acid monomers join together to form proteins Hair, horns, skin, muscles, enzymes Proteins • Amino Acids-20 types-carbon, hydrogen, carboxyl, amino, and R GROUP • Dipeptides and Polypeptides • Enzymes Cause reactions to occur Amino Acids join together by peptide bonds L i p i d s •Do not dissolve in water •Higher ration of Carbon/Hydrogen to Oxygen than carbohydrates •Can store larger amounts of energy Fatty Acids -ends are water opposite -saturated: carbon have 4 bonds -unsaturated: some carbontocarbon (double) Lipid Types • Triglycerides-3 fatty acids to an alcohol glycerol -Saturated=butter/red meat fat -UNsat.=germinating plants • Phospholipids-2 fatty acids vs. 3 -cell membrane • Waxes-waterproof, earwax, plant leaf coating • Steroids-hormones -cholestorol -component of cell membrane Nucleic Acids oDNA Found in the nucleus of cells oRNA Transfers information out of nucleus oMade of nitrogen base, phosphate, and sugar oNitrogen Bases=A&T, G&C Chapter Review • • • • • • Organic/Inorganic Functional Groups Monomer, Polymers, Macromolecules Hydrolysis, Condensation Reaction ATP Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids Resources Internet Sites: http://www.contexo.info/DNA_Basics/Cell_Chemistry.htm http://www.creation-science-prophecy.com/amino/index.html http://www.du.edu/~jcalvert/phys/organic.htm http://www.chem.lsu.edu/lucid/courseinfo/chem1002/ch14.html http://www.ntnu.no/~krill/mineralogee/10.htm http://ithacasciencezone.com/chemzone/lessons/03bonding/dogbonds.htm http://www.biology-books.com/Standard/standard.html#options http://www.picsearch.com/info.cgi?q=hydrolysis&cid=782937693146 http://www.picsearch.com/info.cgi?q=carbohydrates&cid=694883773391 http://www.pemms.co.uk/laughs.html (science jokes) http://www.urlbaron.com/FreeGreetingsCards_fun_cow_jokes.htm (cow jokes)