* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
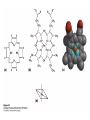
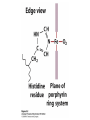
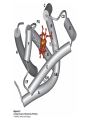
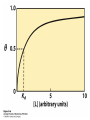
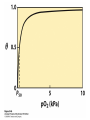
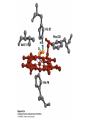
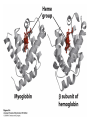
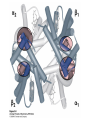
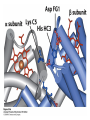
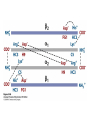
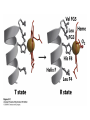
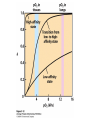
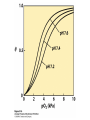
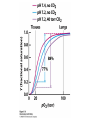
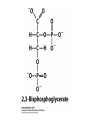
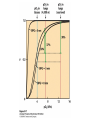
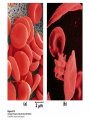
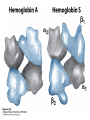
Protein Function Myoglobin & Haemoglobin © 2008 W. H. Freeman and Company Spectroscopic Detection of Oxygen Binding to Myoglobin The heme group is a strong chromophore that absorbs both in ultraviolet and visible range Ferrous form (Fe2+ ) without oxygen has an intense Soret band at 429 nm Oxygen binding alters the electronic properties of the heme, and shifts the position of the Soret band to 414 nm Binding of oxygen can be monitored by UV-Vis spectrophotometry Deoxymyoglobin (in venous blood) appears purplish in color and oxymyoglobin (in arterial blood) is red Binding: Quantitative Description Consider a process in which a ligand (L) binds reversibly to a site in the protein (P) P + ka L The kinetics of such a process is described by: association rate constant ka kb PL the the dissociation rate constant kd After some time, the process will reach the equilibrium where the association and dissociation rates are equal The equilibrium composition is characterized by the the equilibrium constant Ka ka [P] [L] kd [PL] ka [PL] Ka [ P ] [ L] k d Binding: Analysis in Terms of the Bound Fraction • In practice, we can often determine the fraction of occupied binding sites [PL] [PL] [P] • Substituting [PL] with Ka[L][P], we’ll eliminate [PL] K a [L][ P] K a [L][ P] [P] • Eliminating [P] and rearranging gives the result in terms of equilibrium association constant: • In terms of the more commonly used equilibrium dissociation constant: [ L] [ L] 1 Ka [ L] [ L] K d Binding: Graphical Analysis The fraction of bound sites depends on the free ligand concentration and Kd In a typical experiment, ligand concentration is the known independent variable Kd can be determined graphically or via least-squares regression [ L] [ L] K d [L] [L]total Binding: Thermodynamic Connections Interaction strength can be expressed as: – association (binding) constant Ka, units M-1 – dissociation constant Kd, units M, Kd = 1/Ka – interaction (binding) free energy Go, units: kJ/mol Definitions: – Go = Ho -TSo : enthalpy and entropy – Ka = [PL]/[P][L] Kd=[P][L]/[PL] Relationships: – Go = -RT ln Ka = RT ln Kd Magnitudes – Strong binding: Kd < 10 nM – Weak binding: Kd > 10 M (RT at 25 oC is 2.48 kJ/mol) Salt bridges and Hydrogen Bonds in Hemoglobin All these interactions abolished in transition from deoxy to oxy Hb Mutant Hemoglobin s What can be learned from experiments of nature? Mutant hemoglob ins provide unique opportunities to probe structurefunction relation s in a protein. There are nearly 500 known mutant hemoglobin s and >95% represent singl e amino acid substitutions. About 5% of the population carries a variant hemoglobin. Some mutant hemoglobin s cause serious illn ess. The structure of hemoglobin is so delicately balanced that small changes can render the mutant protein nonfunction al. Mutations that lead to loss of heme Heme prosthetic group can be dislodg ed by mutation s in heme binding pocket. In Hb Hammersmith [Phe(42)Ser] the normal Phe in HbA at position 42 in chain is converted to Ser. In HbA, Phe blocks access of water to the heme pocket, but smaller, polar Ser in Hb Hammersmith allo ws water to enter heme pocket. This causes heme to be dislodg ed from pocket, producing a nonfunction al protein. In Hb Kansas [Asn(102)Thr] a critical hydrogen bond in the 1-2 interface between 2-Asn(102) and 1-Asp(94) that stabili zes the R state is lost. Thus the R-T equilibriu m is shifted toward the T state. Hb Kansas has low O2 affinity (P50 = 70 mm Hg = about 9.3 kPa). Little cooperativity in O2 binding (Hill coefficient = 1.3). 1 subnit is red and 2 subunit is green stabilizes the Fe+3 state protects the iron from becoming oxidi zed, has been replaced by Glu, which This is Hb Milwaukee [His(87)Glu] in which the distal His, which normally Crocodile Hemoglobin Crocodil es can remain under water for up to one hour and usually kill their prey by drowning them. How do crocodile's tissues get O2 while submerged? Unlik e deep diving whales, which use myoglobin to store O2 in muscle, crocodil es rely on a unique allo steric effector of Hb to ensure deliv ery of O2 to tissues. While submerged, metabolism produces CO2, which is converted to HCO3 and it is the HCO3 that acts as the allost eric effector by binding to residues at the 12 interface in deoxy Hb and stabili zing the deoxy Hb. This unique allo steric effect is only found in crocodil e Hb. Crocodil e Hb does not bind BPG due to mutations in the BPG-binding pocket