* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indirect cholinergic agonists
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
CCR5 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
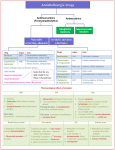
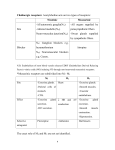
Overview • - Indirect cholinergic agonism (AchE inhibition) • - Muscarinic antagonism (emphasis on drugs and organ effects) • - Nicotine-Ach receptor (emphasis on drugs and therapeutics) Indirect cholinergic agonists Inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase -Increase acetylcholine concentration and lifetime by inhibiting degradation -Act by binding to AchE active site causing reversible (non covalent) or long lasting (covalent modification) Mechanisms of indirect agonism - Quaternary alcohols (ephodronium) – reversible binding (limit acetylcholine access) Non covalent – enzyme-inhibitor complex lifetime (2 - 10 minutes) - Carbamate esters – neostigmine, physostigmine – reaction with AchE active site Covalent carbamoylation – enzyme-inhibitor complex lifetime (0.5 - 6h) - Organophosphates – Parathion, Sarin, Soman - phophorylates AchE active site Covalent phosphorylation – very stable enzyme-inhibitor complex, days (especially after aging) AchE Inhibitors (quaternary alcohols and carbamates) Organophosphates Aging Organ effects/therapeutic uses • - Effects are due to acetylcholine accumulation and are both sympathetic and parasympathetic USES Approx Duration ALCOHOLS Edrophonium Myasthenia gravis arrythmias 5 – 15 minutes Myasthenia gravis Myasthenia gravis Glaucoma Glaucoma 0.5 – 2h 3 – 6h 0.5 – 2h 4 – 6h Glaucoma 100 h (> 4 days) CARBAMATES Neostigmine Pyridostigmine Physostigmine Demecarium Organophosphates Echotiophate Treatment of organophosphate poisoning • 1 - maintenance of vital signs (respiration particularly important) • 2 - Decontamination (to avoid further absorption) • 3 - Atropine parenterally (to minimize muscarinic effects) as required • 4 - Rescue of AchE activity with Hydroxylamines (Pralidoxime, Diacetylmonoxime) Muscarinic antagonism Attropa belladona Muscarinic Antagonists ATROPINE SCOPOLAMINE Muscarinic Antagonists ATROPINE SCOPOLAMINE Attropa belladona - Atropine and Scopolamine are belladona alkaloids (competitive inhibitors) -Drugs differ in their CNS effects, scopolamine permeates the blood-brain barrier -At therapeutic doses atropine has negligible effects upon the CNS, scopolamine even at low doses has prominent CNS effects. Mechanism of drug action - Competitively block muscarinic receptors - Salivary, bronchial, and sweat glands are most sensitive to atropine - Smooth muscle and heart are intermediate in responsiveness - In the eye, causes pupil dilation and difficulty for far vision accomodation - Relaxation of the GI, slows peristalsis History/sources • Atropa belladona - used in the renaissance • Deadly nightshade - used in the middle ages to produce prolonged poisoning Jimson plant leaves burned in India to treat Asthma (1800) purification of atropine (1831) Effect of muscarinic inhibitor in the eye Pupil dilation vs accomodation Effect of muscarinic inhibition in the heart and salivary glands - Increases the heart rate after a transient bradychardia at the low dose - Diminishes gland excretory function Graphic summary of atropine effects Organ effect – drug review Antidotes • ORGAN DRUG APPLICATION Benztropine Treat Parkinson’s disease Scopolamine Prevent/Reduce motion sickness Eye Atropine Pupil dilation Bronchi Ipatropium Bronchodilate in Asthma, COPD GI Methscopolamine Reduce motility/cramps GU Oxybutinin Treat transient cystitis Postoperative bladder spasms CNS Toxicity of muscarinic antagonists • “DRY AS BONE, RED AS A BEET, MAD AS HATTER.” • Dry is a consequence of decreased sweating, salivation and lacrimation • Red is a result of reflex peripheral (cutaneous) vasodilation to dissipate heat (hyperthermia) • Mad is a result of the CNS effects of muscarinic inhibition which can lead to sedation, amnesia (hypersensitivity), or hallucination Nicotinic – Acetylcholine Receptor polarized Relaxation depolarized contraction Signaling through Ach-nicotinic receptor (competitive and depolarizing blockers) Competitive/depolarizing Competitive Physically blocks Ach binding INHIBITOR Depolarizing Binds and locks the receptor open Examples of competitive/depolarizing drugs Competitive Mivacurium Tubocurarine Depolarizing AchE Butyrylcholinesterase Sensitive sites Succinylcholine Clinical uses • Adjuvant use in surgical anesthesia (muscular relaxation) • Advantage – much lighter levels of anesthesia required • Other uses: muscular relaxation for orthopedics (correction of dislocation/alignment of fractures) • (short duration) – facilitate intubation, laryngoscopy, bronchoscopy, esophagoscopy • Control of muscular spasms, strabism, hemifacial spasms, oromandibular and cervical dystonia, spasms of the lower esophageal sphincter • Cosmetic – Bottox (Botulinum toxin A) • Paralytic action on skeletal muscle Agents/Features/Duration • AGENT CLASS PROPERTY ONSET DURATION Succinylcholine Dicholine ester Depolarization 1 min 5 – 8 min Tubocurarine Competitive 5 min 80 – 120 min 30 – 60 min Alkaloid Atracurium Benzylisoquinoline Competitive 3 min Mivacurium Benzylisoquinoline Competitive 3 min 12 – 18 min Pancuronium Ammonio Steroid Competitive 5 min 120 – 180 min Vecuronium Competitive 3 min 60 – 90 min Ammonio Steroid Hydrolysis by esterases Liver clearance/renal elimination Both Precautions/Toxicity • - Prolonged apnea, cardiovascular collapse Sequence of paralysis : Eye muscles, Jaw, Larynx, limbs and trunk, intercostal muscles and the dyaphragm - Generally caused by diminished esterase activity, renal malfunction, liver insufficiency, poor circulatory function. - Special caution in patients with electrolyte imbalance (K+) - Antidote : Neostigmine/Ephodronium to increase Ach, and atropine to block Ach muscarinic stimulation. - Malignant hyperthermia – results from a discharge of Ca2+, exacerbated muscular action – tachycardia, hyperthermia, acidosis and rigidity (mutations of RYR1, central core disease) treated with Dantrolene, preservation of respiration Summary Tetrodoxin Batrachotoxin Hemicholinium Botulinum toxin Curare alkaloids Snake venom α Dantrolene AchE inhibitors Ach pilocarpine Muscarine Bethanechol Neostigmine** Edrophonium** Atropine Scopolamine Tubocurarine Mivacurium X X X X X ** Indirect Movie http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yd46Hs7pTow Nicotine in the brain