* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychopharmacology
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
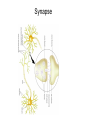
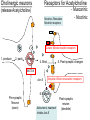
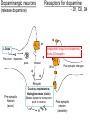
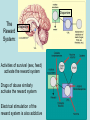
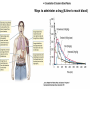
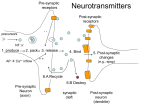
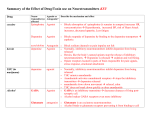
Neurotransmitters • Many Neurotransmitters (NT) exist: - Dopamine Adrenaline Serotonin Acetylcholine • Drugs can either: – Increase the effect of certain neurotransmitter (agonist) – Decrease the effect of certain neurotransmitter (antagonist) Acetylcholine curare Belladonna (atropine) Synapse Receptors for Acetylcholine Cholinergic neurons (release Acetylcholine) Nicotine: Stimulates Nicotinic receptors - Muscarinic - Nicotinic Curare: Blocks nicotinic receptors 1. produce 2. pack 3. release 4. Bind 5. Post-synaptic changes BOTOX Ach-E Atropine: Blocks muscarinic receptors 6.B Destroy Pre-synaptic Neuron (axon) Alzheimer’s treatment Inhibits Ach-E Post-synaptic neuron (dendrite) Acetylcholine (Ach) • Important for: – – – – – Muscle myasthenia gravis (Antagonist, blocker) Vigilance Nicotine mimics Ach effect in brain (Agonist) Memory Anti-cholinesterase drugs for Alzheimer’s disease (Agonist) Learning Anticholinergic drugs (to prevent vomit) (Antagonist) Autonomic Nervous System dopamine Dopaminergic neurons Receptors for dopamine - D1, D2, D4 (release dopamine) D2 L-Dopa Antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia Blocks D2 receptors Precursor dopamine pack D2 release Bind Recycle Pre-synaptic Neuron (axon) Cocaine, amphetamine, Methylphenidate (ritalin) Makes dopamine transporter work in reverse Post-synaptic changes D1 Post-synaptic neuron (dendrite) Dopamine (DA) • Important in: – Movement control – Schizophrenia (?) – ADHD – Drug addiction • • death of dopaminergic cells in Parkinson’s disease anti-psychotic drugs (antagonists) metylphenidate (ritalin) amphetamine, cocaine (agonist) Schizophrenia treatment causes motor problems (as in parkinson’s) Parkinson’s treatment causes hallucinations (as in schizophrenia) Dopamine The Reward System: Dopamine Activities of survival (sex, feed) activate the reward system Drugs of abuse similarly activate the reward system Electrical stimulation of the reward system is also addictive Electrical intracranial self-stimulation stimulation Olds & Milner (1954) n. accumbens The mind is its own place, and in itself, can make heaven of Hell, and a hell of Heaven. dopamine (Satan, in John Milton’s Paradise Lost, book 1, ll. 254–5) Quoted by R. Cardinal VTA Dopamine is released: during sexual behavior but also in anticipation of sex (watching porn) while eating yummy food but also in anticipation of food (picture) but also when seeing cocaine context when doing cocaine Craving: – In rats, one injection activates dopaminergic neurons in reward system of the abstinent rat (‘the first one is free’), causing craving and relapse Relapse – Stressful stimuli increases animal’s susceptibility to relapse Noradrenaline & Adrenaline Oh no! my sympathetic nervous system is overactive again! Serotonin (5-HT) • Important in: – Depression • Receptors: – Way too many! • Drugs: – Fluoxetine (prozac): inhibitor of reuptake (recycle) (SSRI) – LSD: agonist of 5-HT2A – Ectasy: agonist for serotonin and agonist for noradrenaline GABA • Is the most pervasive inhibitory NT in the brain • Drugs: – Benzodiazepines (valium): GABA Agonist • • • • reduces anxiety, promotes sleep, anti-convulsant, muscle relaxant – Alcohol: GABA agonist • Don’t drink while taking this medication Alcohol • Alcohol acts on three systems: – Dopamine: • causes euphoria, • Addictive power – GABA: • reduces anxiety (at low levels) • Sedative (at higher levels) – Glutamate (NMDA): • memory impairment Tolerance a decreased response due to frequent use. • Metabolic tolerance: faster metabolism of the drug.This is a pharmacokinetic mechanism (e.g., alcohol metabolization by hepatic enzimes) • Cellular-adaptive tolerance: down-regulation of receptors (a pharmacodynamic mechanism) Before drug After Drug Ways to administer a drug (& time to reach blood)