PDF
... The reward system is a collection of brain structures which attempts to regulate and control behavior by inducing pleasurable effects. The reward is an operational concept for describing the positive value that an individual ascribes to an object, behavioral act, or internal physical state, and its ...
... The reward system is a collection of brain structures which attempts to regulate and control behavior by inducing pleasurable effects. The reward is an operational concept for describing the positive value that an individual ascribes to an object, behavioral act, or internal physical state, and its ...
Pharmacology and the Nursing Process, 4th ed. Lilley
... Direct-Acting Dopamine Receptor Agonists (cont’d) ...
... Direct-Acting Dopamine Receptor Agonists (cont’d) ...
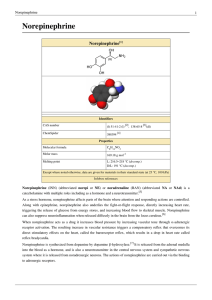
Norepinephrine - Rice CAAM Department
... norepinephrine transporters from taking their respective neurotransmitters back to their storage vesicles for later use. If the norepinephrine transporter normally recycles some dopamine too, then SNRIs will also enhance dopaminergic transmission. Therefore, the antidepressant effects associated wit ...
... norepinephrine transporters from taking their respective neurotransmitters back to their storage vesicles for later use. If the norepinephrine transporter normally recycles some dopamine too, then SNRIs will also enhance dopaminergic transmission. Therefore, the antidepressant effects associated wit ...
Dopamine, behavioral economics, and effort
... in response costs (i.e., ratio requirements). Moreover, interference with accumbens DA transmission exerts a powerful influence over effort-related choice behavior. Rats with accumbens DA depletions or antagonism reallocate their instrumental behavior away from food-reinforced tasks that have high r ...
... in response costs (i.e., ratio requirements). Moreover, interference with accumbens DA transmission exerts a powerful influence over effort-related choice behavior. Rats with accumbens DA depletions or antagonism reallocate their instrumental behavior away from food-reinforced tasks that have high r ...
Review
... routine patient monitoring: arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and limb or cutaneous ischemia. Data Abstraction ...
... routine patient monitoring: arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and limb or cutaneous ischemia. Data Abstraction ...
Biological substrates of reward and aversion: A nucleus accumbens
... Theories about its role in motivation have been a critical element in our understanding of addiction (e.g., Wise and Bozarth, 1987; Wise and Rompré, 1989). There are three primary lines of evidence implicating the NAc in reward, involving pharmacological, molecular, and electrophysiological approac ...
... Theories about its role in motivation have been a critical element in our understanding of addiction (e.g., Wise and Bozarth, 1987; Wise and Rompré, 1989). There are three primary lines of evidence implicating the NAc in reward, involving pharmacological, molecular, and electrophysiological approac ...
Clinical pharmacology of dobutamine and dopamine in preterm
... contraction. The chronotropic effect is useful for the treatment of arrhythmias whereas the inotropic effect is useful to augment the myocardial contractility. Dobutamine is about four times as potent as dopamine in stimulating myocardial contractility in low concentrations and increases left ventri ...
... contraction. The chronotropic effect is useful for the treatment of arrhythmias whereas the inotropic effect is useful to augment the myocardial contractility. Dobutamine is about four times as potent as dopamine in stimulating myocardial contractility in low concentrations and increases left ventri ...
Dopamine, Locus of Control, and the Exploration
... is a matter of luck’). Other biological factors may also be at play. Previously, we demonstrated that the amount of exploration that subjects undertake varies with a functional polymorphism (Val158Met) in the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene, which degrades synaptically released dopamine. In ...
... is a matter of luck’). Other biological factors may also be at play. Previously, we demonstrated that the amount of exploration that subjects undertake varies with a functional polymorphism (Val158Met) in the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene, which degrades synaptically released dopamine. In ...
PDF - Circulation
... inotropic drug infusion, cardiac outputs and pressures were measured at 5 and 10 min. After 10 min the first drug dosage was changed to the next higher increment of the same drug unless systolic arterial pressure was greater than 140 torr, in which case the initial dosage was halved. After an additi ...
... inotropic drug infusion, cardiac outputs and pressures were measured at 5 and 10 min. After 10 min the first drug dosage was changed to the next higher increment of the same drug unless systolic arterial pressure was greater than 140 torr, in which case the initial dosage was halved. After an additi ...
Serotonin 2A Receptors Differentially Contribute to Abuse
... pronounced reinstatement of behavior in nonhuman primates (Andersen et al., 2010). To examine the role of 5-HT2A receptors in drug- and cue-induced reinstatement, M100907 (0.3 mg/kg, i.m.) or its vehicle was administered 1 h before the cocaine prime. The effects of M100907 in this reinstatement were ...
... pronounced reinstatement of behavior in nonhuman primates (Andersen et al., 2010). To examine the role of 5-HT2A receptors in drug- and cue-induced reinstatement, M100907 (0.3 mg/kg, i.m.) or its vehicle was administered 1 h before the cocaine prime. The effects of M100907 in this reinstatement were ...
Viral restoration of dopamine signaling to the dorsal striatum
... the tongue correlated with bursts of electrophysiological activity (action potential spikes) from 60–80% of dopamine neurons recorded. However, after repeated cue–reward pairings, dopamine neuron activation occurred in response to the conditioned cue instead of during presentation (and consumption) ...
... the tongue correlated with bursts of electrophysiological activity (action potential spikes) from 60–80% of dopamine neurons recorded. However, after repeated cue–reward pairings, dopamine neuron activation occurred in response to the conditioned cue instead of during presentation (and consumption) ...
Characterization of the Effects of the Partial Dopamine Agonist
... Basic preclinical studies have implicated dopamine neurotransmission as a critical determinant in the acute reinforcing properties of psychostimulant drugs and in the increase in reward threshold associated with abstinence from cocaine abuse, two major components of the psychostimulant dependence cy ...
... Basic preclinical studies have implicated dopamine neurotransmission as a critical determinant in the acute reinforcing properties of psychostimulant drugs and in the increase in reward threshold associated with abstinence from cocaine abuse, two major components of the psychostimulant dependence cy ...
The Dopamine Transporter and Cocaine Medication Development
... number of drug injections delivered per session. Both measures are influenced by the schedule of reinforcement and drug dose. Moreover, most self-administered drugs have direct effects on rate of responding that may be distinct from their reinforcing effects. For example, cocaine injections may incr ...
... number of drug injections delivered per session. Both measures are influenced by the schedule of reinforcement and drug dose. Moreover, most self-administered drugs have direct effects on rate of responding that may be distinct from their reinforcing effects. For example, cocaine injections may incr ...
Amphetamine Paradoxically Augments Exocytotic Dopamine Release and Phasic Dopamine Signals
... above that elicited by natural rewards is proposed to cause overlearning of cues predicting drug availability and underlie a “pathological usurpation” of reward-related learning mechanisms during addiction (Hyman et al., 2006). While it is attractive to postulate that all abused drugs enhance phasic ...
... above that elicited by natural rewards is proposed to cause overlearning of cues predicting drug availability and underlie a “pathological usurpation” of reward-related learning mechanisms during addiction (Hyman et al., 2006). While it is attractive to postulate that all abused drugs enhance phasic ...
Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla
... Vasoconstriction occurs in most systemic arteries and veins (postjunctional a 1 and a 2 ...
... Vasoconstriction occurs in most systemic arteries and veins (postjunctional a 1 and a 2 ...
Antipsychotic Drugs - Pharmacological Reviews
... some of the earlier studies used ligands related to spiperone (e.g., [11C]N-methylspiperone). The binding properties of these ligands are such that they do not reach equilibrium at the receptors during the scan, and this leads to problems in the interpretation of experiments that will be considered ...
... some of the earlier studies used ligands related to spiperone (e.g., [11C]N-methylspiperone). The binding properties of these ligands are such that they do not reach equilibrium at the receptors during the scan, and this leads to problems in the interpretation of experiments that will be considered ...
The placebo effect in Parkinson`s disease
... two studies to have focused on the placebo effect in Parkinson’s disease both found the effect to be strong [37,38]. Dopamine, expectation and reward ...
... two studies to have focused on the placebo effect in Parkinson’s disease both found the effect to be strong [37,38]. Dopamine, expectation and reward ...
Dopamine and glucose, obesity, and reward deficiency syndrome
... reward and negative eating behaviors in obesity are accompanied by diminished dopaminergic neurotransmission. Bariatric surgery the most successful therapy for obesity rapidly reduces hunger and improves satiety, the mechanisms are unknown and little is known about dopaminergic activity following th ...
... reward and negative eating behaviors in obesity are accompanied by diminished dopaminergic neurotransmission. Bariatric surgery the most successful therapy for obesity rapidly reduces hunger and improves satiety, the mechanisms are unknown and little is known about dopaminergic activity following th ...
Reinforcement, Dopamine and Rodent Models in Drug
... which is correlated with the rate of learning. Third, this strengthening effect of dopamine has precise timing requirements, such that delays in the dopamine pulse result in the loss of strengthening effect. We summarize the evidence for these points in the following. This complex and emerging liter ...
... which is correlated with the rate of learning. Third, this strengthening effect of dopamine has precise timing requirements, such that delays in the dopamine pulse result in the loss of strengthening effect. We summarize the evidence for these points in the following. This complex and emerging liter ...
Modulation of ventral tegmental area dopamine receptors inhibit
... dopamine neurons, including the ventral tegmental area (VTA) which is a key area that controls nicotine dependence processes. In this study, the role of dopamine D1 and D2/3 receptors of the VTA on anxiogenic-like behavior induced with intra-CeA injection of nicotine has been investigated. Male Wist ...
... dopamine neurons, including the ventral tegmental area (VTA) which is a key area that controls nicotine dependence processes. In this study, the role of dopamine D1 and D2/3 receptors of the VTA on anxiogenic-like behavior induced with intra-CeA injection of nicotine has been investigated. Male Wist ...
Targeting the dopamine D receptor in schizophrenia
... explored for the mode of action of chlorpromazine, including its action on mitochondrial enzymes, sodium–potassium-ATPase and related enzymes, as well as its membrane-stabilising action, such as its strong potency to inhibit membrane action potentials, and to stabilise cellular and subcellular membr ...
... explored for the mode of action of chlorpromazine, including its action on mitochondrial enzymes, sodium–potassium-ATPase and related enzymes, as well as its membrane-stabilising action, such as its strong potency to inhibit membrane action potentials, and to stabilise cellular and subcellular membr ...
Role for Reactive Oxygen Species in Methamphetamine Modulation
... formation of melanins in dopaminergic cells. We explore this link more fully here. In an in vitro system, oxidative species (including Fe3+, an inorganic catalyst for oxidative stress), enhance the rate of melanization of DA. Methamphetamine increased oxidative stress in an in vivo model. Additional ...
... formation of melanins in dopaminergic cells. We explore this link more fully here. In an in vitro system, oxidative species (including Fe3+, an inorganic catalyst for oxidative stress), enhance the rate of melanization of DA. Methamphetamine increased oxidative stress in an in vivo model. Additional ...
Control of Extracellular Dopamine at Dendrite and Axon Terminals
... Figure 1. A single stimulus evoked more dopamine release in the striatum than the VTA, yet the time course of release is similar. A, A single stimulation was used to evoke dopamine release in the VTA (n ⫽ 10; gray trace) and the dorsal striatum (n ⫽ 6; black trace). A single stimulation produced ⬃20 ...
... Figure 1. A single stimulus evoked more dopamine release in the striatum than the VTA, yet the time course of release is similar. A, A single stimulation was used to evoke dopamine release in the VTA (n ⫽ 10; gray trace) and the dorsal striatum (n ⫽ 6; black trace). A single stimulation produced ⬃20 ...
Chronic Treatment with Dopamine Receptor Antagonists
... gm; Simonsen) were iniected (i.n.) with EEDO (8 mrr/ka) freshlv dissolved in ethr&ol/wate; (1:l voi/vol) or vehicle alone. To determine whether EEDQ had the same EC,, for D, and D, dopamine receptors, a dose-response for EEDQ was performed, in which rats received 1 mg/ kg, 2 mg/kg, or 4 mg/kg EEDQ. ...
... gm; Simonsen) were iniected (i.n.) with EEDO (8 mrr/ka) freshlv dissolved in ethr&ol/wate; (1:l voi/vol) or vehicle alone. To determine whether EEDQ had the same EC,, for D, and D, dopamine receptors, a dose-response for EEDQ was performed, in which rats received 1 mg/ kg, 2 mg/kg, or 4 mg/kg EEDQ. ...
Dopaminergic involvement during mental fatigue in
... disengagement of the dACC, additional, compensatory regions may need to be recruited for task completion. Although time-on-task effects could stem from cognitive processes beyond fatigue, alternative processes including practice effects or target familiarity would ostensibly improve performance. One ...
... disengagement of the dACC, additional, compensatory regions may need to be recruited for task completion. Although time-on-task effects could stem from cognitive processes beyond fatigue, alternative processes including practice effects or target familiarity would ostensibly improve performance. One ...
Dopamine
Dopamine is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families that plays a number of important roles in the human brain and body, as well as elsewhere in biology. Its name derives from its chemical structure: it is an amine formed by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of L-DOPA. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by nerve cells to send signals to other nerve cells. The brain includes several distinct dopamine systems, one of which plays a major role in reward-motivated behavior. Most types of reward increase the level of dopamine in the brain, and a variety of addictive drugs increase dopamine neuronal activity. Other brain dopamine systems are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones.Several important diseases of the nervous system are associated with dysfunctions of the dopamine system. Parkinson's disease, a degenerative condition causing tremor and motor impairment, is caused by loss of dopamine-secreting neurons in a midbrain area called the substantia nigra. There is evidence that schizophrenia involves altered levels of dopamine activity, and the antipsychotic drugs that are frequently used to treat it have a primary effect of attenuating dopamine activity. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and restless legs syndrome are associated with decreased dopamine activity.Outside the nervous system, dopamine functions in several parts of the body as a local chemical messenger. In the blood vessels, it inhibits norepinephrine release and acts as a vasodilator (at normal concentrations); in the kidneys, it increases sodium excretion and urine output; in the pancreas, it reduces insulin production; in the digestive system, it reduces gastrointestinal motility and protects intestinal mucosa; and in the immune system, it reduces the activity of lymphocytes. With the exception of the blood vessels, dopamine in each of these peripheral systems has a ""paracrine"" function: it is synthesized locally and exerts its effects on cells that are located near the cells that release it.A variety of important drugs work by altering the way the body makes or uses dopamine. Dopamine itself is available for intravenous injection: although it cannot reach the brain from the bloodstream, its peripheral effects make it useful in the treatment of heart failure or shock, especially in newborn babies. L-DOPA, the metabolic precursor of dopamine, does reach the brain and is the most widely used treatment for Parkinson's disease. Dopaminergic stimulants can be addictive in high doses, but some are used at lower doses to treat ADHD. Conversely, many antipsychotic drugs act by suppressing the effects of dopamine. Drugs that act against dopamine by a different mechanism are also some of the most effective anti-nausea agents.