* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Kantian ethics wikipedia , lookup
Divine command theory wikipedia , lookup
Individualism wikipedia , lookup
Bernard Williams wikipedia , lookup
Ethics in religion wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Role-taking theory wikipedia , lookup
On the Genealogy of Morality wikipedia , lookup
Moral psychology wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
The Moral Landscape wikipedia , lookup
The Sovereignty of Good wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Moral responsibility wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
Critique of Practical Reason wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Moral development wikipedia , lookup
Moral relativism wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg wikipedia , lookup
Secular morality wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
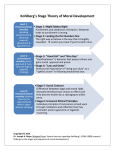
Psychological Aspects of Lord of the Flies Sigmund Freud’s Basic Elements of Personality SUPEREGO EGO ID ID • Dominated by the PLEASURE PRINCIPLE • Demands immediate gratification of desires regardless of undesirable effects • Equated with the unconscious • (“Id”) EGO • Dominated by the REALITY PRINCIPLE • Evolves from id • Suppresses inappropriate desires • (“Ego”) SUPEREGO • Dominated by morality, spirituality, ethical principle • Serves as the censor on the ego’s functions • Comprises the ideals derived from the values of family and society • The source of guilt and fear of punishment • (“Superego”) Lawrence Kohlberg’s Levels and Stages of Moral Development • • • • Preconventional Morality Conventional Morality Postconventional Morality (“Kohlberg’s Levels and Stages”) Preconventional Morality Moral value resides in a person’s own needs and wants • Stage 1 – Obedience and Punishment Orientation – Moral judgment is motivated by a need to avoid punishment • Stage 2 – Instrumental-Relativist Orientation – Moral judgment is motivated by a need to satisfy own desires (“Kohlberg’s Levels and Stages”) Conventional Morality Moral values reside in performing good or right roles, in maintaining the convention order, and in pleasing others • Stage 3 – “Good Boy/Girl” Orientation – Moral judgment is motivated by a need to avoid rejection or disapproval from others • Stage 4 – Law and Order Orientation – Moral judgment is motivated by a need to not be criticized by a true authority figure (“Kohlberg’s Levels and Stages”) Postconventional Morality • Stage 5 Moral values reside in principles. – Legalistic Orientation – Moral judgment is motivated by community respect for all, respecting social order, and living under legally determined law • Stage 6 – Universal, Ethical Orientation – Moral judgment is motivated by one’s own conscience (“Kohlberg’s Levels and Stages”) Simon Piggy Ralph Jack/Roger Works Cited “Ego,” Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2000 http://encarta.msn.com 1997-2000 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. “Id,” Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2000 http://encarta.msn.com 1997-2000 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. “Superego,” Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2000 http://encarta.msn.com 1997-2000 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. “Lawrence Kohlberg’s Levels and Stages of Moral Development.” Pepperdine University. 28 September 2000 <http://gsep.pepperdine.edu/gsep/class/ethics/kohlberg/Stages_Mo ral-Development.html>.