* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12 notes - Andrews University
Postdevelopment theory wikipedia , lookup
World Englishes wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
MOGUL framework wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Universal grammar wikipedia , lookup
Role-taking theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
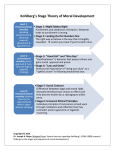
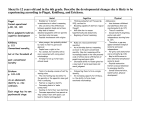
Chapter 12 notes I. Define concrete operational thought. a. This is one of Piaget’s views, which is characterized by a collection of logical concepts that enable children to reason logically about things and events that one perceives. II. Explain the logical principles: a. Classification i. The logical principle by which things are organized into groups according to some property they have in common. b. Identity i. The principle that certain characteristics of an object remain the same even if other characteristics change. c. Reversibility i. The principle that sometimes a thing that has been changed can be returned to its original states by reversing the process by which it was changed. d. Reciprocity i. The principle that two things may change in opposite ways in order to balance each other out. III. Describe Kohlberg’s Stages of moral development. a. Level 1 is the Preconvention moral reasoning. i. Stage one: might makes right, important things are obedience to authority. ii. Stage two: look out for number one, this means each person tries to take care for his or her own needs. b. Level 2 is the Conventional moral reasoning. i. Stage three: Good girl and nice boy, Social approval is more important than any reward. ii. Stage four: Law and order, Proper behavior means obeying the law and been a good citizen. c. Level 3 is the Postconventional moral reasoning. i. Stage five: Social contract. One should obey social rules because they benefit everyone and are established by mutual agreement. ii. Stage six: Universal ethical principles. General universal principles, not individual situations or community practices, determine right or wrong. Ethical values are established by individual reflection and may contradict the egocentric. IV. Identify criticisms of Kohlberg’s theory of moral development. a. Some critics believe that level 3 reflects only liberal, western intellectual values. Some cultures may not move up Kohlberg’s hierarchy as fast as others. Also another is that Kohlberg overlooked significant gendered differences. V. Cite Carol Gilligan’s criticism of Kohlberg’s theory of moral development. a. Gilligan explains that Kohlberg overlooked significant gender differences. She says that females develop a morality of care more than a morality of justice. The morality of care makes girls and women reluctant to judge right or wrong in absolute terms because hey are socialized to be nurturing, compassionate, and nonjudgmental. VI. Define information processing theory and how it relates to selective attention. a. This is an approach to understand cognition. The theory is useful because people can learn anything, sense or nonsense, and it helps scientist understand the mechanisms of such learning. 11 year olds are better thinkers than 7. People use mental processes to perform three functions: to search for specific units of information when needed, to analyze situations, and to express the analysis in a format that another person can understand. VII. Differentiate among sensory memory, working memory, and long-term memory. a. Sensory memory: i. This is part of the information system where incoming stimulus information is stored for a split second to allow it to be processed. b. Working memory i. The part in which current conscious mental activity occurs. Also called short-term memory. c. Long-term memory i. The part in which virtually limitless amounts of information can be stored indefinitely. VIII. Define selective attention and metacognition. a. Selective attention i. Part of the control process that has the ability to screen out distraction and focus on the details that will help in later recall of information. b. Metacogntion i. Part of the control process that is “thinking about thinking,” or the ability to evaluate cognitive task to determine how best to accomplish it, and then to monitor and adjust one’s performance on that task. IX. Differentiate between the phonics approach and the whole language approach to teaching reading. a. The phonic approach requires children to learn the sound of each letter before they begin to decipher simple words. b. Whole-language approach encourages the children to develop all their language skills-talking and listening, reading and writing—all with the goal of communication. X. Define total immersion and how it relates to language. a. Total immersion is the approach to teaching a second language in which instruction occurs entirely in that language and the learner’s native language is not used at all. XI. Describe the following strategies of teaching English. a. English as a second language: i. Requires all non-English-speaking students to undergo an intensive instructional period together, with the goal of mastering the basics of English in six months or so. The teacher doesn’t speak nor allows the students to speak in their native language. b. Bilingual Education i. Requires that the teacher instructs the children in school subjects using their native language as well as English.